-
Article
-
Analyzing the Effects of a Floor-type Pedestrian Signal Assist Device on Pedestrian Safety Using the Difference-in-Difference-in-Differences Method
삼중차분법을 이용한 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치의 보행 안전 개선효과 분석
-
JEONG, Bokyoung, NA, Hyeon, LEE, Sugie
정보경, 나현, 이수기
- This study examines the impact of a floor-type pedestrian signal assist device on pedestrian traffic safety in Seoul using the Difference-in-Difference-in-Differences(DDD) method. …
본 연구는 삼중차분법을 활용하여 서울시를 대상으로 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치가 보행자 교통안전 개선에 미친 효과를 확인하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 나아가, 주·야간에 바닥형 보행신호등 …
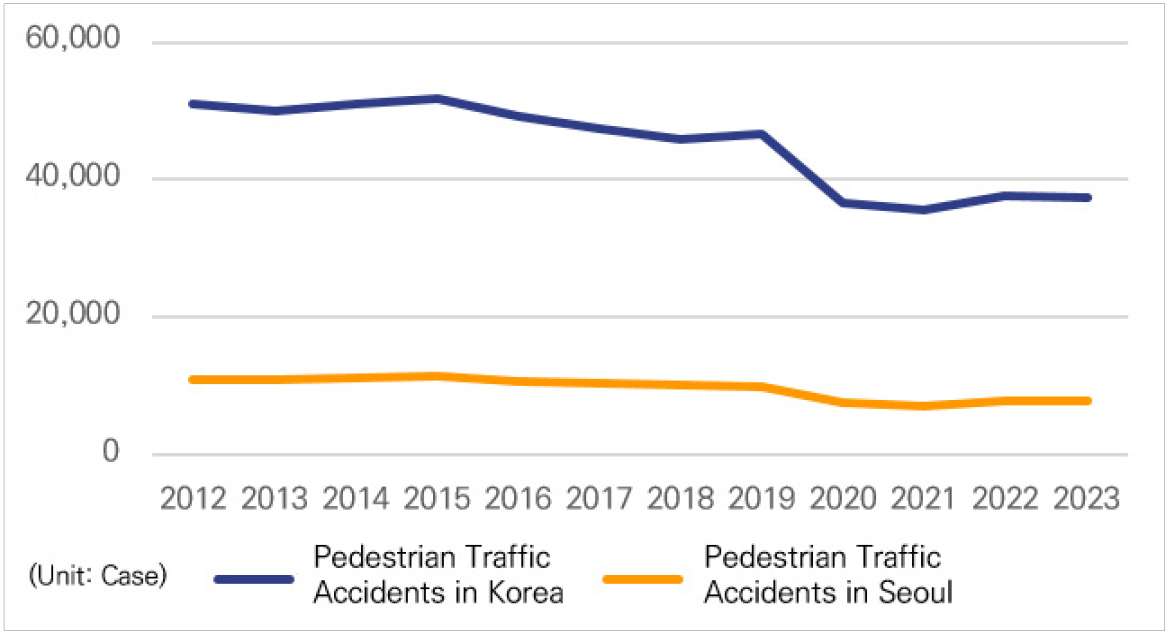
- This study examines the impact of a floor-type pedestrian signal assist device on pedestrian traffic safety in Seoul using the Difference-in-Difference-in-Differences(DDD) method. Furthermore, it aims to identify whether the effects of these devices differ between daytime and nighttime, with the goal of enhancing their practical effectiveness and contributing to the improvement of pedestrian environments. In light of growing concerns about “Smombie” (smartphone+ zombie)—pedestrians distracted by smartphone use—these devices have been introduced to improve pedestrian safety. However, empirical studies on their actual effectiveness in reducing pedestrian accidents remain limited. The study covers the periods from 2015 to 2017 (pre-installation) and from 2021 to 2023 (post-installation), with the unit of analysis set at 100-meter grid cells across Seoul. First, Propensity Score Matching was conducted to select comparable treatment and control groups and to confirm the parallel trends assumption. Subsequently, the difference-in-difference-in-differences method was applied to estimate the policy effect. The results show that the installation of floor-type pedestrian signal assist devices did not have a significant impact on reducing pedestrian accidents during the daytime. However, during nighttime, the devices were associated with a statistically significant decrease in accidents, suggesting a time-specific policy effect. This study contributes to the literature by providing empirical evidence on the effectiveness of floor-type pedestrian signal assist devices, offering policy implications for enhancing pedestrian safety.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 삼중차분법을 활용하여 서울시를 대상으로 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치가 보행자 교통안전 개선에 미친 효과를 확인하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 나아가, 주·야간에 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치의 영향이 차이가 있는지 확인하며 본 보조장치의 실효성을 높이고, 보행환경의 발전에 기여하고자 한다. 최근 보행 중 휴대전화를 사용하는 사람들을 두고 스몸비(Smombie)라는 신조어가 등장할 만큼 보행안전 분야에서 그 심각성이 증가하고 있다. 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치는 이러한 스몸비족의 보행안전에 도움을 주기 위해 도입되었으나, 해당 보조장치가 실제로 보행자 교통사고 감소에 효과가 있는지에 관한 실증연구는 부족한 실정이다. 본 연구의 시간적 범위는 2019년 바닥형 보행신호등이 도입되기 전후 3년인 2015년부터 2017년까지, 2021년부터 2023년까지이다. 공간적 범위는 서울시이며 분석 단위는 100m 격자로 설정하였다. 먼저 성향점수매칭을 실시하여 처치군과 대조군을 선정해 평행추세가정을 확인 후, 삼중차분법을 적용해 정책 효과를 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치의 설치는 주간 시간대 보행자 교통사고 건수 감소에 유의미한 영향이 나타나지 않았으나, 야간 시간대의 경우 사고 건수 감소에 유의한 영향을 미친 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구는 바닥형 보행신호등 보조장치의 효과를 실증적으로 분석하여 보행자 안전에 대한 정책적 시사점을 제시하였다는 점에서 의의가 있다.
-
Analyzing the Effects of a Floor-type Pedestrian Signal Assist Device on Pedestrian Safety Using the Difference-in-Difference-in-Differences Method
-
Article
-
Latent Class Analysis and Severity Model Evaluation for Vehicle-to-Vehicle Crashes in Urban Areas
도심부 차대차 사고 잠재계층분석 및 심각도 모형 평가
-
KIM, Woowon, LEE, Sungjun, PARK, Juneyoung, CHO, Junhan
김우원, 이성준, 박준영, 조준한
- With the rapid growth of cities and increasing vehicle penetration, safety in urban areas has become an important social issue. In particular, …
도시의 급속한 성장과 차량 보급의 증가로 인해 도심부 교통안전은 중요한 사회적 과제로 대두되고 있다. 특히 왕복 4~5차로 도로는 진출입부, 교차로 등 다양한 …
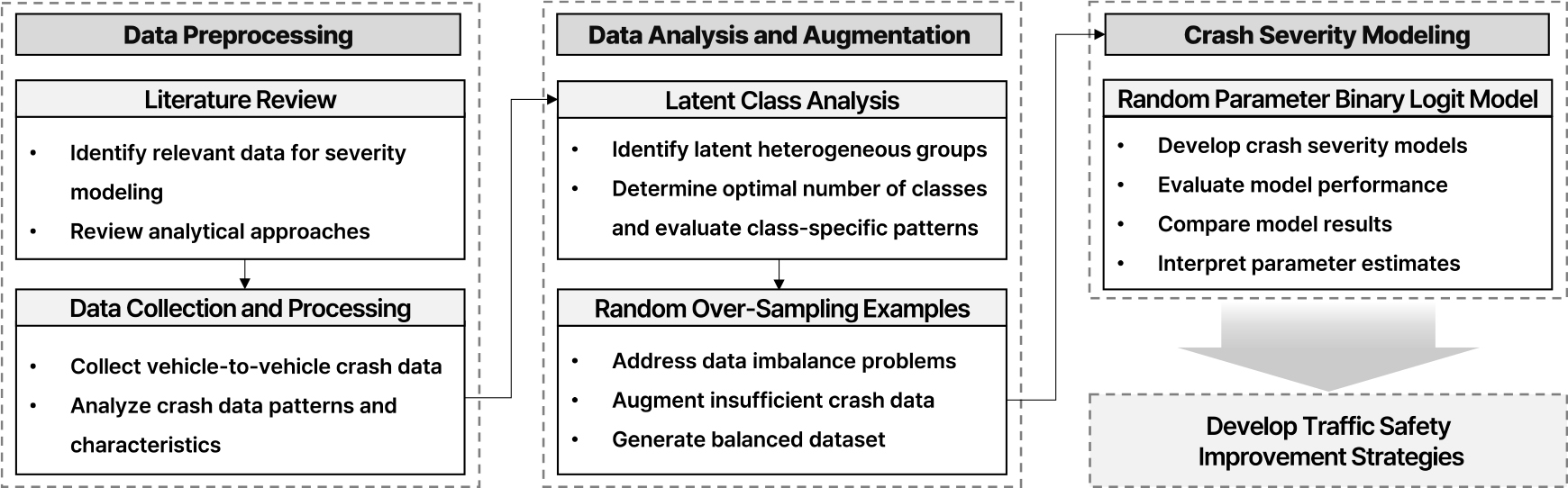
- With the rapid growth of cities and increasing vehicle penetration, safety in urban areas has become an important social issue. In particular, 4-5 lane section shows a complex pattern due to various road components such as intersections, and tends to increase the severity of crashes due to high driving speeds. In addition, various factors such as increased traffic volume during peak hours and frequent lane changes due to staggered sections increase the risk of crashes. Considering these complex factors, this study aims to analyze the main factors influencing the severity of 4-5 lane urban road crashes. A total of 212 vehicle-to-vehicle crash cases were collected from dashcam footage on 4-5 lane urban dual carriageways across the country in 2021. Latent Class Analysis was conducted to capture latent heterogeneity in crash patterns. Additionally, to address data shortage, the dataset was augmented using the Random Over-Sampling Examples method. Subsequently, both the Binary Logit Model and the Random Parameter Binary Logit Model were estimated to analyze the factors influencing crash severity. The analysis identified two primary latent classes: Class 1 was dominated by rear-end crashes occurring on snowy or wet road surfaces, while Class 2 was characterized by side-impact crashes occurring under clear weather and dry surface conditions. Key determinants of crash severity included type of crash, road surface condition, and time period. Notably, both models indicated that rainy weather conditions were associated with elevated predicted crash severity, and wet and snowy road surfaces also showed significant associations with increased severity. Furthermore, the Random Parameter model outperformed the fixed-effect model across all performance metrics indicating that accounting for unobserved class yields more effective insights into crash severity. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of targeted safety strategies aimed at improving the safety of urban 4-5 lane roadways.
- COLLAPSE
도시의 급속한 성장과 차량 보급의 증가로 인해 도심부 교통안전은 중요한 사회적 과제로 대두되고 있다. 특히 왕복 4~5차로 도로는 진출입부, 교차로 등 다양한 요소가 밀집되어 있으며, 높은 주행 속도와 빈번한 차로 변경으로 인해 사고 발생 시 심각도가 높아질 가능성이 크다. 본 연구는 도심부 왕복 4~5차로에서 발생한 차대차 사고를 대상으로 사고 심각도에 영향을 미치는 주요 요인을 식별하고 이질적 특성을 고려한 분석을 목적으로 한다. 이를 위해 2021년 전국 도심부 왕복 4~5차로 구간에서 발생한 교통사고 중 블랙박스 영상으로 수집된 212건의 사고 데이터를 분석에 활용하였다. 사고의 잠재적 이질성을 반영하기 위해 잠재계층분석을 수행하였으며, 데이터의 부족 문제를 완화하기 위해 Random Over-Sampling Examples 기법으로 데이터를 증강하였다. 이후 이항 로짓 모델과 랜덤 파라미터 이항 로짓 모델을 적용하여 사고 심각도에 미치는 영향 요인을 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 사고 데이터는 두 개의 주요 계층으로 분류되었으며, 계층 1은 적설 및 젖은 노면 상태에서 발생한 후미추돌 사고가 지배적인 특성을 보였고, 계층 2는 맑은 날씨와 건조한 노면에서 발생한 측면 추돌이 분포하는 특성을 나타냈다. 심각도에 영향을 미치는 주요 요인은 사고 유형, 노면 상태, 시간대 등으로 도출되었으며, 특히 두 모델 모두 비가 오는 기상 조건에서 높은 사고 심각도 추정값이 도출되었다. 또한 노면이 습윤 및 적설 상태 역시 심각도 증가와 유의한 관련성을 보였다. 랜덤 파라미터 모델이 여러 평가지표에서 우수한 성능을 보임에 따라, 개별 사고의 이질성을 반영한 방식이 사고 심각도 분석에 효과적임을 알 수 있었다. 이러한 결과를 통해 도심부 왕복 4~5차로의 안전성 향상을 기대할 수 있다.
-
Latent Class Analysis and Severity Model Evaluation for Vehicle-to-Vehicle Crashes in Urban Areas
-
Article
-
Development of a Fuel Efficiency Prediction Model for Autonomous Eco-Driving and Analysis of Road Environment Effects
자율주행 기반 경제운전의 연비 예측모형 및 도로환경 영향 분석
-
LEE, Kyu Jin
이규진
- In the recent years, the internet has become accessible without limitation of time and location to anyone with smartphones. It resulted in …
본 연구는 자율주행 기반 경제운전 로직 설계에 필요한 기초자료를 제공하기 위해, 자동차 연비에 영향을 미치는 운전자 제어 행태와 도로교통 환경 요인을 통합적으로 …
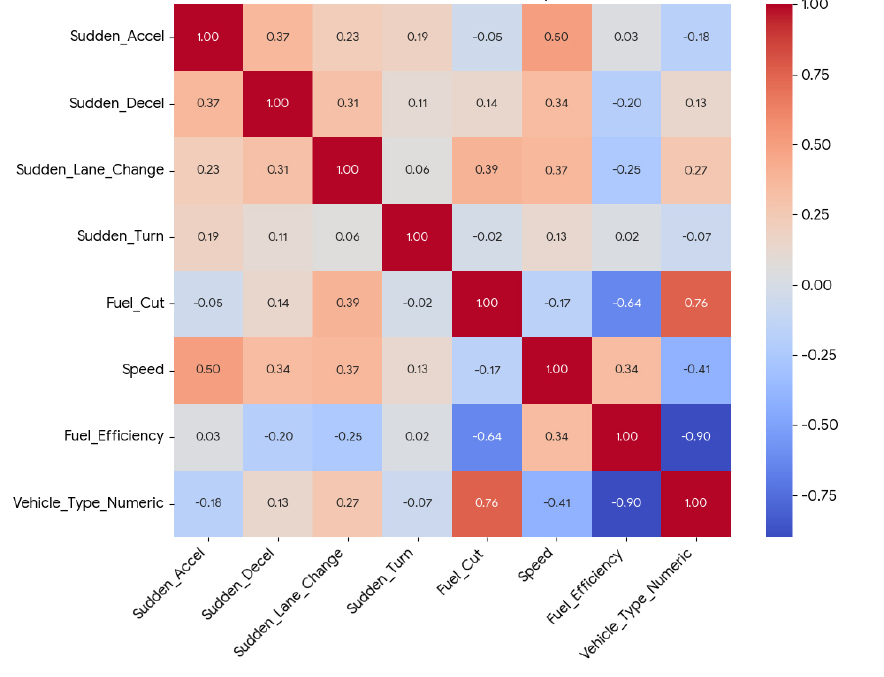
- In the recent years, the internet has become accessible without limitation of time and location to anyone with smartphones. It resulted in more convenient travel information access This study aims to support the design of eco-driving-based autonomous driving systems by analyzing the combined effects of driver control behavior and roadway conditions on vehicle fuel efficiency, and by developing vehicle-specific fuel economy prediction models. First, real-world driving data from 980 passenger cars and vans were analyzed using a Classification and Regression Tree (CART) approach to quantify how the frequency of control variables—such as rapid acceleration and fuel cut usage—impacts fuel economy. The results revealed that key predictors and their thresholds vary by vehicle type, highlighting the need for tailored autonomous driving control logic based on vehicle characteristics. Next, approximately 170,000 operational records from bus tachographs were used to construct a mixed-effects model that statistically examined the structural influence of road and vehicle factors. The analysis showed that the effect of eco-driving practices significantly varies depending on service area and bus type. In particular, under congested urban conditions, external factors such as frequent stops and traffic signals tend to reduce the fuel-saving benefits of eco-driving. These findings suggest that autonomous driving systems should evolve beyond driver substitution to incorporate “context-aware” strategies responsive to the operating environment. From a technical standpoint, this study provides quantitative evidence to inform the development of eco-driving algorithms for autonomous vehicles. From a policy perspective, it also underscores the importance of addressing environmental barriers through road infrastructure improvements to enhance the effectiveness of fuel-saving strategies.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 자율주행 기반 경제운전 로직 설계에 필요한 기초자료를 제공하기 위해, 자동차 연비에 영향을 미치는 운전자 제어 행태와 도로교통 환경 요인을 통합적으로 분석하고, 차종별 연비 예측모형을 구축하였다. 먼저, 승용차 및 승합차 980대의 실운행 데이터를 활용해 분류 및 회귀 트리(CART) 분석을 수행하고, 급가속, 퓨얼컷 등 제어 변수의 빈도가 연비에 미치는 영향을 정량적으로 규명하였다. 분석 결과, 연비에 영향을 미치는 주요 변수와 그 임계값은 차종별로 상이하게 나타났으며, 이는 차량 특성에 따른 자율주행 제어 로직의 맞춤화 필요성을 시사한다. 이어서 약 17만 건의 버스 운행기록계 데이터를 활용해 혼합효과 모형을 구축한 결과, 운행 권역과 차량 유형에 따라 경제운전 효과가 유의한 차이를 보였다. 특히 도심에서는 정체, 신호 간섭 등 외적 요인으로 인해 경제운전의 연비 개선 효과가 제한되는 경향이 나타났다. 이는 자율주행 시스템이 단순한 운전자 대체 기술을 넘어, 주행 환경을 고려하는 상황인지형 제어 전략으로 발전해야 함을 의미한다. 본 연구는 기술적 측면에서 자율주행 기반 경제운전 알고리즘 개발에, 정책적 측면에서는 도로 인프라 개선을 통한 연비 저해 요인 해소에 기여할 수 있는 실증적 근거를 제시하였다.
-
Development of a Fuel Efficiency Prediction Model for Autonomous Eco-Driving and Analysis of Road Environment Effects
-
Article
-
An Explanatory Analysis of Spatial Structure of Seoul Metropolitan Area Based on Individual Mobility Characteristics: An Application of Multivariate Spatial Statistics
개인 단위 모빌리티 특성 기반 수도권 공간구조 분석: 다변량 공간통계기법을 중심으로
-
SHIM, Jiyun, LEE, Jae Hyun
심지윤, 이재현
- The Seoul Metropolitan Area (SMA) operates as a functionally integrated region, yet reveals spatial disparities in population composition, industrial structure, and mobility …
수도권은 광역화된 하나의 경제 및 생활권으로 권역 내 위치한 도시 및 지역 간 상호작용이 활발한 지역이다. 그러나 이들 지역은 인구구조, 산업구조, 생활양식 …
- The Seoul Metropolitan Area (SMA) operates as a functionally integrated region, yet reveals spatial disparities in population composition, industrial structure, and mobility behavior. Despite this, spatial understanding grounded in residents' daily activities and travel patterns—which could inform effective metropolitan planning—remains limited. This study examines the spatial autocorrelation of multidimensional mobility indicators to identify similarity and heterogeneity in residents’ travel patterns across the SMA. To this end, we utilize multidimensional mobility indicators that summarize individuals’ travel behaviors and conduct global and local Moran’s I analyses for both univariate and bivariate cases. The results reveal two contrasting spatial clusters: peripheral Gyeonggi regions characterized by long-distance, long-duration, monotonous, and elongated trips, and central Seoul characterized by short-distance, short- duration, complex, and circular trips. We find that the gravitational pull of central Seoul extends into surrounding Gyeonggi regions. These findings highlight practical evidence for developing policies that reflect the unique characteristics of regions within the Seoul Metropolitan Area.
- COLLAPSE
수도권은 광역화된 하나의 경제 및 생활권으로 권역 내 위치한 도시 및 지역 간 상호작용이 활발한 지역이다. 그러나 이들 지역은 인구구조, 산업구조, 생활양식 등에서 상당한 차이가 나타나고 있다. 이에 따라 수도권 광역계획은 지역의 연계와 조화를 도모함과 동시에, 각 지역의 특성을 차별적으로 반영하여야 한다. 그러나, 이러한 계획 수립에 근거로 쓰일 수 있는 지역주민들의 일상생활 활동-통행 특성에 기반한 공간구조에 대한 이해는 미진한 실정이다. 따라서, 본 연구는 수도권 거주자의 모빌리티 특성을 공간적으로 분석하여 지역별 패턴의 유사성과 이질성을 이해하고자 하였다. 이를 위해 개개인의 복잡한 통행행태 특성을 요약하여 나타낼 수 있는 다차원 모빌리티 지표를 이용하여, 일변량 및 이변량에 대해 전역적, 국지적 Moran’s I 공간통계 분석을 수행하였다. 분석 결과, 장거리·장시간 통행 및 단순장종(長縱)형 패턴이 나타나는 경기 외곽 클러스터와, 단거리·단시간 통행 및 복잡원형형 패턴을 보이는 서울 중심 클러스터가 도출되었다. 이와 함께 수도권 중심부의 유인력이 인근 경기 지역까지 미치고 있음을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 공간적 자기상관 기반의 모빌리티 분석을 통해 수도권 내 지역 특성을 반영한 정책 수립의 실질적 근거를 제공할 수 있을 것이다.
-
An Explanatory Analysis of Spatial Structure of Seoul Metropolitan Area Based on Individual Mobility Characteristics: An Application of Multivariate Spatial Statistics
-
Article

-
An Analysis of Congestion Patterns at Bus Exclusive Lane Stations Using Soft-DTW Based Clustering
Soft-DTW 기반 클러스터링을 활용한 중앙버스전용차로 정류장 정체 유형 분석
-
PARK, Su Jin, YANG, Jaehwan
박수진, 양재환
- The Seoul Metropolitan Government has implemented median bus exclusive lanes across 13 arterial corridors to enhance the operational efficiency of its bus …
서울시는 버스의 효율적 운영을 위해 13개 도로축에서 중앙버스전용차로를 운영 중에 있으나, 광역버스 증가와 입석금지 등 정책 변화, 수도권 광역화에 따른 수요 증가로 …
- The Seoul Metropolitan Government has implemented median bus exclusive lanes across 13 arterial corridors to enhance the operational efficiency of its bus system. However, recent policy changes, including a ban on standing passengers on intercity buses and the increasing demand resulting from metropolitan expansion, have led to growing congestion and a decline in bus speed competitiveness. This study analyzes 20 major bus stations located along Seoul’s median bus exclusive lanes, using data from the Bus Management System and field observation records. To quantify congestion characteristics during the morning and evening peak hours, the study applies time-series clustering based on Soft Dynamic Time Warping. The analysis identifies four distinct congestion types according to the underlying causes of delay, and proposes improvement strategies tailored to the operational conditions of each type. Unlike previous static performance evaluations, this study provides detailed insights into actual operational conditions and offers a foundation for developing customized strategies for bus station management. The findings are expected to support targeted policy interventions by congestion type and contribute to the sustainable operation of the median bus exclusive lane system in Seoul.
- COLLAPSE
서울시는 버스의 효율적 운영을 위해 13개 도로축에서 중앙버스전용차로를 운영 중에 있으나, 광역버스 증가와 입석금지 등 정책 변화, 수도권 광역화에 따른 수요 증가로 인해 혼잡 심화 및 통행속도 경쟁력 저하 등의 문제가 발생하고 있다. 이에 본 연구는 서울시 중앙버스전용차로에 위치한 20개 정류장을 대상으로, BMS 데이터와 현장 관측자료를 활용하여 오전 및 오후 첨두시간대의 정체 특성을 정량화하고, Soft-DTW 기반 시계열 클러스터링을 통해 정체 유형을 분류하였다. 분석 결과, 정체의 발생 원인에 따라 네 가지 유형으로 분류되었으며, 각 유형별 발생 요인과 운영 조건에 적합한 개선방안을 제시하였다. 본 연구는 기존의 정태적 성과 평가를 넘어, 실제 운영 현황에 기반한 정밀 진단을 통해 맞춤형 정류장 운영전략 수립의 기초자료를 제공한다는 점에서 의의가 있다. 향후 정류장별 혼잡 유형에 따른 전략적 정책 개입과 중앙버스전용차로 운영의 지속 가능성 확보에 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
An Analysis of Congestion Patterns at Bus Exclusive Lane Stations Using Soft-DTW Based Clustering
-
Article
-
An Integrated Assessment Framework for Energy, Climate, and Air Costs in Road Transportation
도로교통의 에너지·기후·대기 통합비용 평가체계
-
LEE, Kyu Jin, CHOI, Yoonhyuk
이규진, 최윤혁
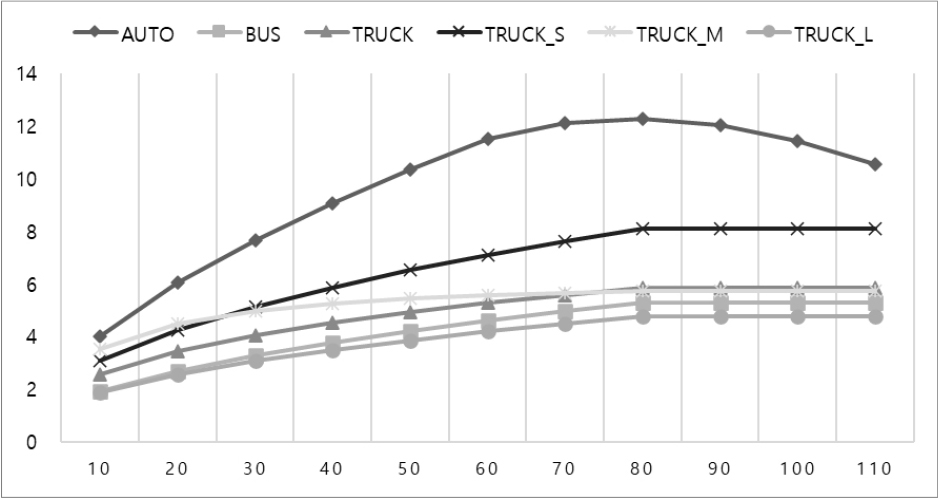
- This study establishes an Integrated evaluation framework to quantify the costs associated with energy consumption and emissions of greenhouse gases and air …
본 연구는 도로교통 부문에서 발생하는 에너지 및 온실가스·대기오염물질 배출 비용을 정량화하기 위한 평가체계를 구축하고, 지역·차종·속도별로 에너지·기후·대기 비용을 분석하였다. 에너지 비용은 에너지 총조사 …
- This study establishes an Integrated evaluation framework to quantify the costs associated with energy consumption and emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants in the road transport sector. It analyzes energy, climate, and air quality costs by vehicle type, driving speed, and regional characteristics. Energy costs were estimated using real-world fuel efficiency data derived from the National Energy Survey, combined with a speed-specific CO2 emission coefficient function to improve realism. Climate and air pollution costs were calculated based on nationally certified emission factors reflecting recent vehicle performance. Social cost unit values were estimated using the benefit transfer method from the EU’s Impact Pathway Model, adjusted for Korea’s purchasing power parity (PPP), exchange rate, and GDP growth. The analysis found that energy costs increased by 177% for passenger cars, 212% for buses, and 122% for freight vehicles compared to conventional estimates. Climate and air pollution costs increased by 203%, 227%, and 168%, respectively, due to the application of population exposure-weighted health impacts for major pollutants such as NOx and avoidance cost metrics for CO2. By updating previously underestimated externalities using empirical national data and internationally standardized methodologies, this study presents a scientifically rigorous and policy-relevant evaluation framework. It offers a robust foundation for incorporating environmental and economic performance into national transport project assessments, contributing significantly to sustainable and balanced infrastructure planning.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 도로교통 부문에서 발생하는 에너지 및 온실가스·대기오염물질 배출 비용을 정량화하기 위한 평가체계를 구축하고, 지역·차종·속도별로 에너지·기후·대기 비용을 분석하였다. 에너지 비용은 에너지 총조사 기반의 실연비와 차속별 CO2 배출계수 함수를 활용하여 현실성을 확보하였으며, 기후·대기 비용은 최신 차량의 배출성능을 반영한 국가 공식 배출계수를 기반으로 공학적으로 추정하였다. 배출원의 사회적 피해비용은 EU의 영향경로모형을 국내 여건에 맞게 편익이전기법을 적용하여 산정하였다. 분석 결과, 에너지 비용은 기존 연구(예비타당성 지침 등) 대비 승용차 177%, 버스 212%, 화물차 122% 수준으로 증가하였으며, 기후·대기 비용은 NOx 등 주요 오염물질의 인구노출 기반 피해비용 및 CO2의 회피비용 기반 평가체계를 적용함에 따라, 각각 203%(승용차), 227%(버스), 168%(화물차) 증가한 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구는 그간 과소 평가되어 온 도로교통 부문의 에너지·기후·대기 비용 항목을 실측 기반 자료와 국제 기준에 따라 현행화함으로써, 보다 현실적이고 과학적인 편익·비용 평가체계를 제시하였으며, 국가 교통사업의 환경성과 경제성을 균형있게 반영할 수 있는 분석 기반을 제공하였다는 점에서 학술적·정책적 기여가 크다.
-
An Integrated Assessment Framework for Energy, Climate, and Air Costs in Road Transportation
-
Article
-
A Study on the Effectiveness of Smart School Zone Systems in Child Protection Areas
어린이 보호구역 내 스마트스쿨존 시스템의 효과 분석 연구
-
KIM, DongHyeop, KIM, Jin-Tae
김동협, 김진태
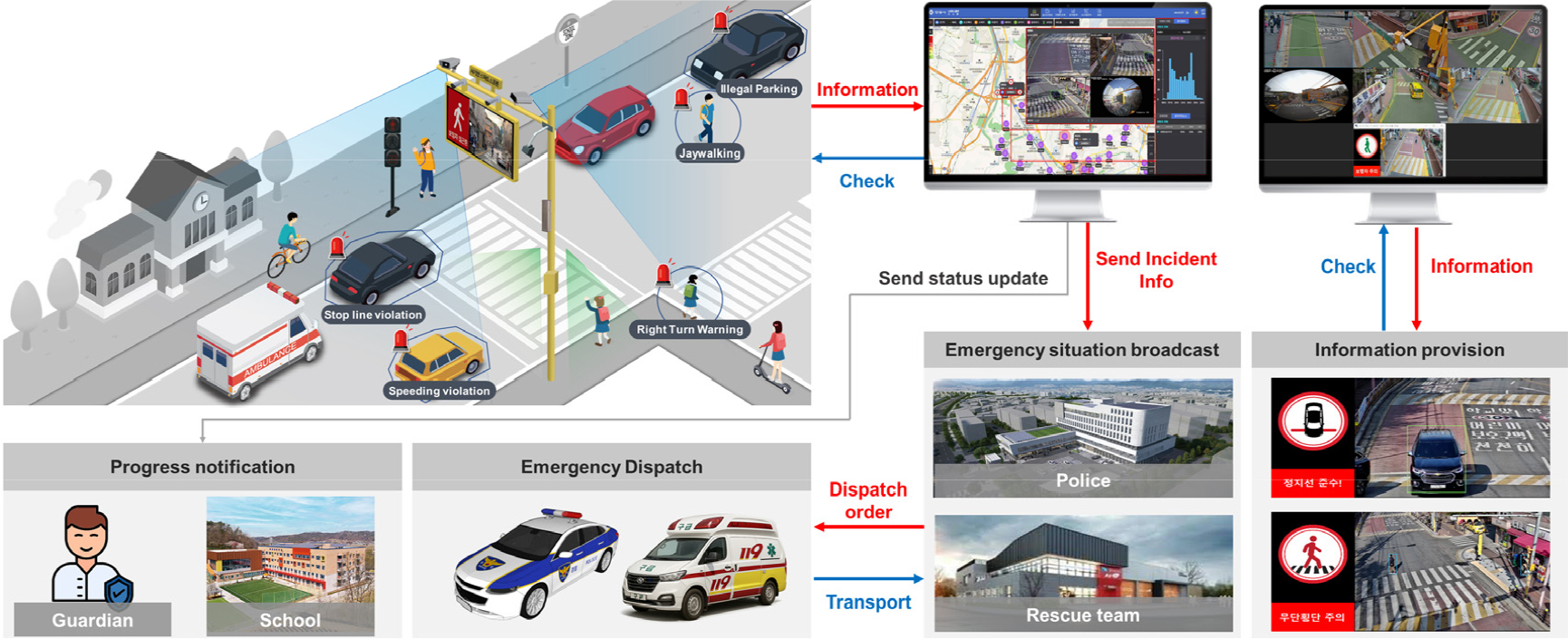
- Traffic accidents within child protection zones continue to occur at a relatively high frequency, attributed to a combination of factors such as …
어린이 보호구역 내에서의 교통사고는 여전히 높은 수준으로 발생하고 있으며, 이는 어린이의 돌발행동, 운전자의 인지 부족, 정적인 안전시설의 한계 등 복합적인 요인에 기인한다. …
- Traffic accidents within child protection zones continue to occur at a relatively high frequency, attributed to a combination of factors such as children’s unpredictable behavior, drivers’ lack of awareness, and the limitations of static safety infrastructure. As a solution to these issues, the integration of AI-based video recognition technologies and real-time warning systems—referred to as Smart School Zone Systems—is increasingly being adopted. This study conducts a quantitative analysis to empirically evaluate the effectiveness of Smart School Zone systems in improving traffic safety within these zones. The analysis targets systems installed around elementary schools in Anyang City, Gyeonggi Province. Data were collected through real-time video detection before and after system deployment for the following service features: speeding alerts, illegal parking guidance, stop line violation warnings, and jaywalking detection. Based on these data, metrics for each service feature were analyzed, and statistical significance tests were conducted to assess changes in traffic and pedestrian behaviors. The results indicated a statistically significant reduction in all three key indicators: the proportion of speeding vehicles decreased by 2.7 percentage points per hour, stop line violations dropped by 0.5 percentage points per hour, and the average number of jaywalking incidents reduced by 5.95 cases per hour. However, the reduction in illegal parking (an average decrease of 0.03 vehicles per hour) was not statistically significant. This was attributed to structural factors in certain commercial and high-density residential areas, as well as nighttime parking demand. Nonetheless, partial improvements were observed during specific time periods and locations, highlighting the need for integration with dedicated illegal parking enforcement systems. This study confirms the potential of Smart School Zone systems as active traffic management technologies that supplement the limitations of conventional static safety infrastructure. The findings serve as foundational data for the advancement of related technologies and future policy development. Further research is suggested to assess long-term effectiveness, evaluate location-based differences in impact, and generalize findings through the inclusion of a broader sample of study sites.
- COLLAPSE
어린이 보호구역 내에서의 교통사고는 여전히 높은 수준으로 발생하고 있으며, 이는 어린이의 돌발행동, 운전자의 인지 부족, 정적인 안전시설의 한계 등 복합적인 요인에 기인한다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위한 대안으로 최근 인공지능 기반 영상인식 기술과 실시간 경고 시스템을 접목한 스마트스쿨존 시스템이 도입되고 있다. 본 연구는 스마트스쿨존 시스템이 어린이 보호구역 내에서 실질적인 교통안전 효과를 제공하는지를 실증적으로 평가하기 위하여 정량적 효과를 분석하였다. 효과 분석은 경기도 안양시 내 초등학교에 설치된 스마트스쿨존 시스템을 대상으로 하였으며 과속경보, 불법 주·정차 계도, 정지선 위반 차량 계도, 무단횡단 감지의 서비스 항목에 대하여 시스템 설치 전·후의 실시간 영상검지를 통하여 데이터를 수집하였다. 이를 바탕으로 각 서비스의 효과척도별 데이터를 수집하고 교통행태 및 보행행태 변화의 통계적 유의성을 검증하였다. 분석결과, 과속차량 비율의 경우 시간당 2.7%p 감소하였으며 정지선 위반 차량의 비율도 시간당 0.5%p 감소하였으며 무단횡단 보행자 수는 시간당 평균 5.95명이 감소하여 세 가지 지표에서 통계적으로 유의미한 감소를 확인하였다. 반면, 불법주정차 차량의 경우 시간당 평균 0.03대가 감소하였지만, 통계적으로 유의하지 않는 것으로 분석되었다. 다만 특정 시간대나 구간에서 부분적인 개선 효과가 존재하였고 일부 상가 및 주거 밀집 지역의 구조적 요인과 야간 주차 수요가 영향을 미친 결과로 해석되어 개선을 위해서는 향후 불법 주·정차 단속시스템과의 연계의 필요성을 확인하였다. 본 연구는 스마트스쿨존 시스템이 정적 교통안전시설의 한계를 보완하는 능동형 교통관리 기술로서의 가능성을 확인하였으며 향후 기술 고도화 및 정책 설계에 활용될 수 있는 기초자료로 활용될 수 있다. 향후에는 장기적인 측면에서의 효과 검증, 설치 위치에 따른 효과 분석, 일반화를 위한 표본 지점 확대를 통한 효과평가의 필요성이 있다.
-
A Study on the Effectiveness of Smart School Zone Systems in Child Protection Areas
-
Article
-
Network Motif Analysis of Public Bicycle Usage in Seoul: A Comparison between High and Low Usage Districts
네트워크 모티프 분석을 활용한 서울시 자치구 공공자전거 이용 구조 비교: 따릉이 사용 상하위 자치구 비교를 중심으로
-
JUNG, Yubin, CHOI, Junyong
정유빈, 최준용
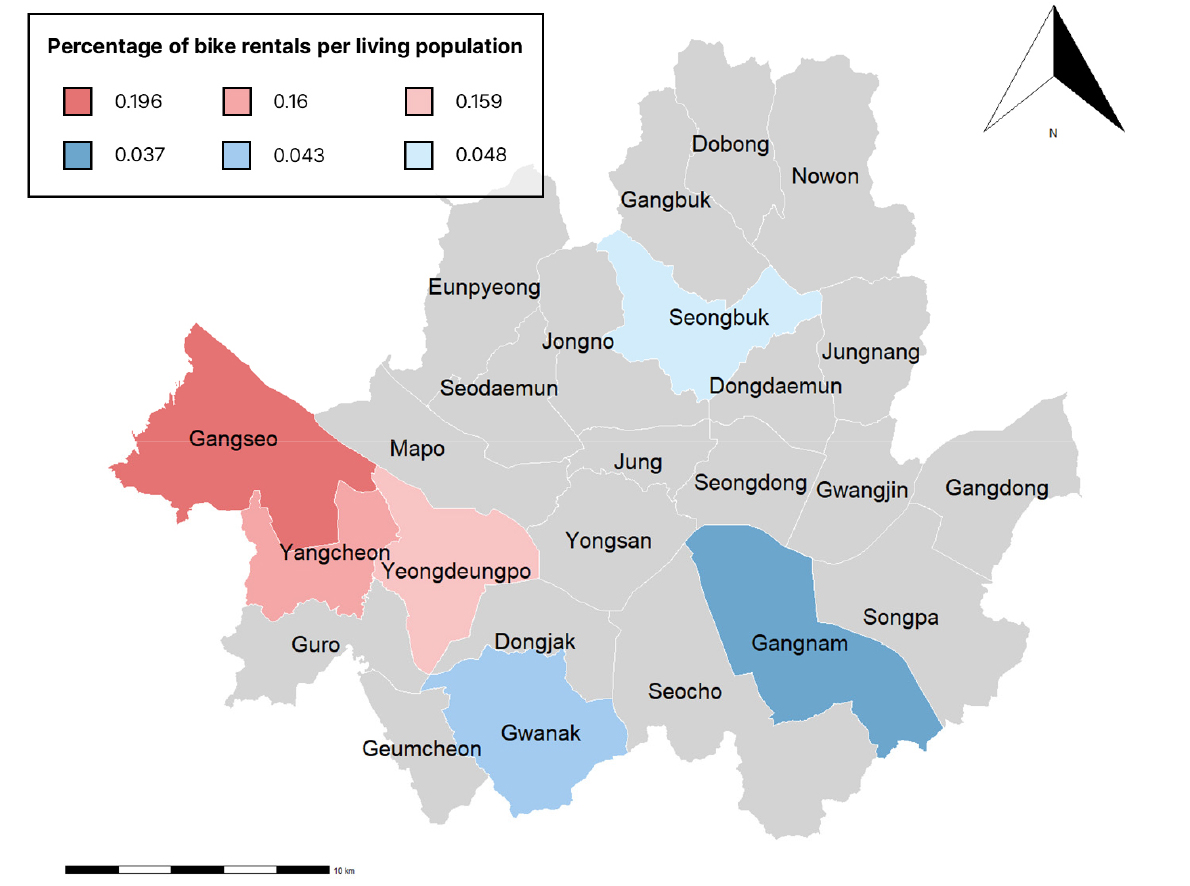
- Seoul’s public bicycle service ‘Seoul Bike’ has been expanding as an eco-friendly mode of transportation, aiming to alleviate traffic congestion, reduce greenhouse …
서울특별시 공공자전거 서비스 ‘따릉이’는 교통 혼잡 완화, 온실가스 감축, 시민 건강 증진을 목적으로 운영되고 있다. 기존 연구는 사회 네트워크 분석을 통해 개별 …
- Seoul’s public bicycle service ‘Seoul Bike’ has been expanding as an eco-friendly mode of transportation, aiming to alleviate traffic congestion, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote public health. Previous studies have mainly evaluated the importance of individual stations using centrality measures in social network analysis. However, centrality measures often fail to capture the overall network structure represented by repeated travel patterns. To address this gap, this study introduces network motif analysis to compare the structural characteristics between high- and low-usage districts in Seoul’s public bicycle network. Network motifs are subgraphs defined as small, recurring connection patterns that occur at different frequencies compared to randomized networks and serve as the fundamental building blocks of complex networks. Using weekday rental and return records from September to October 2024, this study compared the bicycle-sharing networks of three high-usage districts (Gangseo-gu, Yangcheon-gu, Yeongdeungpo-gu) and three low-usage districts (Gangnam-gu, Gwanak-gu, Seongbuk-gu). The results indicate that cyclic motifs, representing reciprocal connections, dominated both groups, whereas simple or one-way connection types were relatively rare. Nevertheless, we can observe distinct tendencies: high-usage districts exhibited a greater proportion of cyclic and bidirectional structures forming cohesive intra-district flows, while low-usage districts displayed hub-like patterns where flows were concentrated toward particular nodes. These findings suggest that the spatial layout and travel demand conditions influence the structural formation and interaction dynamics of the public bicycle network. By applying network motif analysis, this study provides an analytical framework for identifying structurally meaningful and recurrent connection patterns within Seoul’s public bicycle system, offering insights for its operational management and station planning.
- COLLAPSE
서울특별시 공공자전거 서비스 ‘따릉이’는 교통 혼잡 완화, 온실가스 감축, 시민 건강 증진을 목적으로 운영되고 있다. 기존 연구는 사회 네트워크 분석을 통해 개별 정류소의 중심성을 평가하는 데 집중하였으나, 네트워크 전반에서 반복적으로 형성되는 구조적 패턴을 설명하는 데에는 한계가 있었다. 본 연구는 이러한 한계를 보완하기 위해 네트워크 모티프 분석을 도입하여, 2024년 9~10월 평일 데이터를 기반으로 서울시 공공자전거 이용 상위(강서, 양천, 영등포)와 하위(강남, 관악, 성북) 자치구의 네트워크 구조를 비교하였다. 분석 결과, 상하위 자치구 모두에서 순환적 연결을 반영하는 모티프가 안정적으로 나타났으나 단순하거나 제한적인 연결 구조는 거의 드러나지 않았다. 그러나 세부적으로는 상위 자치구에서 복합적이고 순환적인 구조가 일관되게 형성된 반면, 하위 자치구에서는 단순 연쇄 구조가 일부 강조되거나 특정 모티프에서 자치구별 차이가 크게 나타났다. 구조 범주별로 보면, 상위 자치구는 단순형이 거의 관찰되지 않고 허브형과 순환형이 반복적으로 나타나 일관된 생활권 연결망을 형성하였다. 반면 하위 자치구는 생활인구 규모에 비해 이용률이 낮아 모티프별 차이가 크게 드러났으며, 자치구별로 상이한 구조적 특성이 확인되었다. 관악구는 순환형이 두드러지게 강조된 반면, 강남구는 허브형이 뚜렷하고 순환형은 일부에 그쳤으며, 성북구는 특정 구조가 압도적으로 부각되지 않고 여러 유형이 고르게 분포하였다. 본 연구는 자치구 간 네트워크 구성 차이를 식별하고, 공공자전거 네트워크의 구조와 기능을 입체적으로 진단할 수 있는 분석 틀을 제시하였다. 네트워크 모티프 분석을 통해 향후 정류소 배치, 자전거 재배치, 대중교통 연계 강화 등 운영 전략 수립에 기초 자료로 활용될 수 있다.
-
Network Motif Analysis of Public Bicycle Usage in Seoul: A Comparison between High and Low Usage Districts
-
Article
-
A Two-Dimensional Lane-Changing Model with Asymmetric Driving Behavior
비대칭 주행 행태를 반영한 2차원 차로 변경 모델
-
JEON, Sujae, KIM, Yeeun, YEO, Hwasoo
전수제, 김예은, 여화수
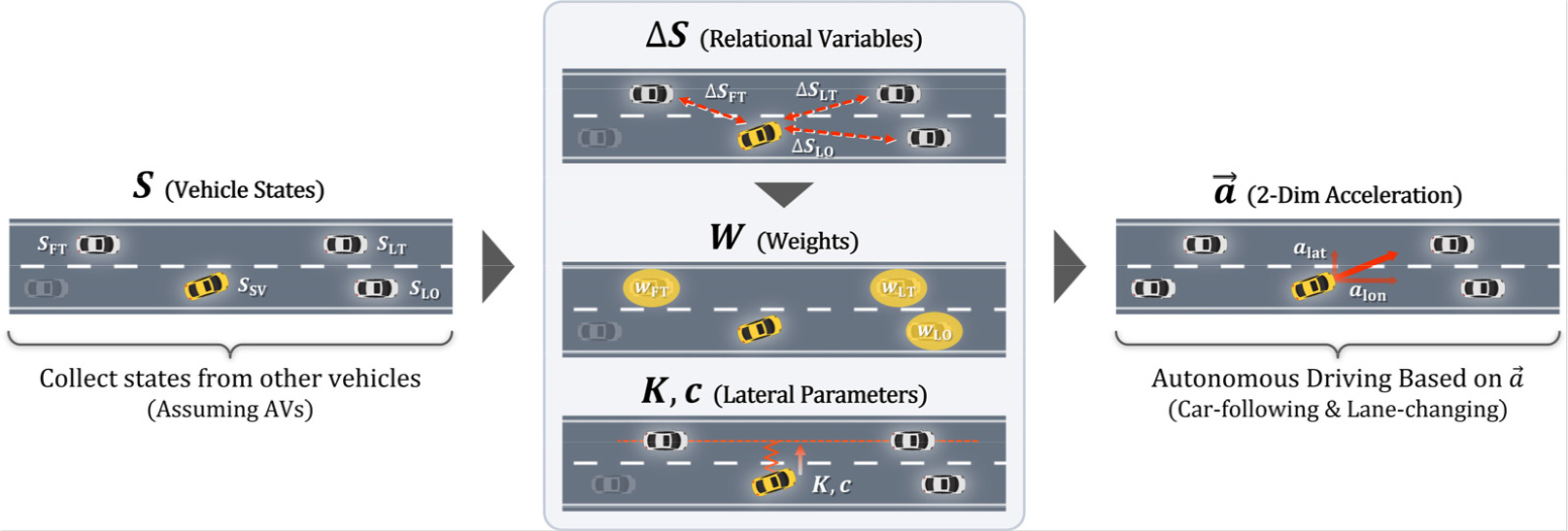
- In recent years, traffic simulation has increasingly required models that capture not only safety and efficiency but also human-like driving behavior. While …
최근 교통 시뮬레이션에서는 안전성과 효율성뿐만 아니라 실제 운전자와 유사한 주행 행태를 재현할 수 있는 모델에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있다. 기존의 다양한 모델들이 …
- In recent years, traffic simulation has increasingly required models that capture not only safety and efficiency but also human-like driving behavior. While numerous models have been proposed to reflect human driving characteristicsm most have focused on one-dimensional car-following, considering only longitudinal movements. However, they lack smooth integration with lane-changing behavior, which restricts their ability to reproduce complex and context-aware driving behaviors. Therefore, this study proposes a two-dimensional driving behavior model that incorporates human-like characteristics. The model calculates both longitudinal and lateral accelerations using relational variables derived from an asymmetric repulsive force model. For longitudinal control, a weight-based approach is employed to simultaneously account for the influence of multiple surrounding vehicles, enabling more complex and human-like driving behavior. For lateral control, the model adopts a spring- mass-damper system, in which the spring coefficient is dynamically adjusted based on surrounding traffic conditions. This allows for flexible responses such as lane-change abandonment or timing adjustments. Simulation results show that the proposed model enables smoother behavior transitions and reduces the impact on surrounding traffic, while also reproducing adaptive behaviors such as lane-change abandonment under unsafe conditions.
- COLLAPSE
최근 교통 시뮬레이션에서는 안전성과 효율성뿐만 아니라 실제 운전자와 유사한 주행 행태를 재현할 수 있는 모델에 대한 수요가 증가하고 있다. 기존의 다양한 모델들이 인간 운전자의 특성을 반영하기 위해 제안되었으나, 대부분은 1차원 차량 추종에 초점을 맞추어 종방향 움직임만을 고려하였다. 그러나 이러한 모델들은 차로 변경 행태와의 매끄러운 통합이 부족하여 복잡하고 상황 인지적인 주행 행태를 재현하는 데 한계가 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 인간과 유사한 특성을 반영한 2차원 주행 행태 모델을 제안한다. 제안된 모델은 비대칭 반발력 모델에서 도출된 관계 변수를 활용하여 종방향 및 횡방향 가속도를 종합적으로 계산한다. 종방향 제어에서는 가중치 기반 접근법을 적용하여 다수의 주변 차량이 미치는 영향을 동시에 고려함으로써 보다 복잡하고 인간적인 주행 행태를 구현한다. 횡방향 제어에서는 주변 교통 상황에 따라 스프링 계수를 동적으로 조정하는 스프링-질량-댐퍼 시스템을 채택하여, 차로 변경 포기나 시점 조정과 같은 유연한 대응이 가능하다. 시뮬레이션 결과, 제안된 모델은 주행 행태 전환을 더욱 부드럽게 하고 주변 교통에 미치는 영향을 줄이며, 안전하지 않은 상황에서의 차로 변경 포기와 같은 적응적 행태를 재현할 수 있음을 보여준다.
-
A Two-Dimensional Lane-Changing Model with Asymmetric Driving Behavior
-
Article
-
Reliability Analysis of Screen Doors and Door’s Maintenance Strategies for Demand Responsive Self-Driving Shuttles
스크린도어 신뢰도 분석과 이를 활용한 수요응답형 자율주행 셔틀의 출입문 유지보수 전략
-
MORRIS, Alain Anthony, KIM, Tae-jin, KIM, Hyun
모리스알레인 안토니, 김태진, 김현
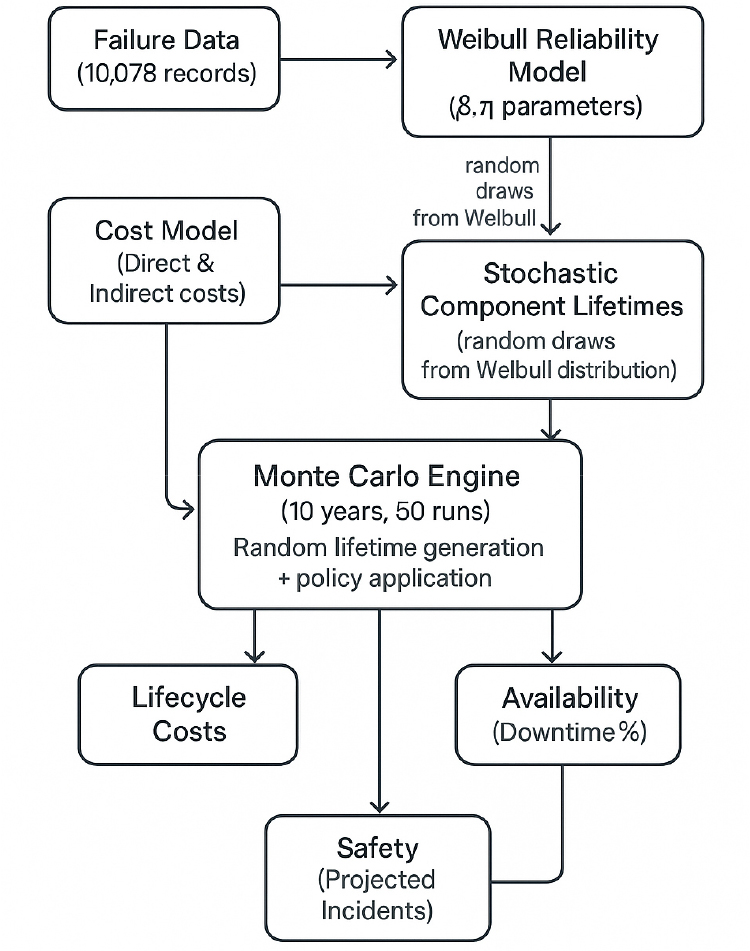
- This study analyzes the reliability and maintenance performance of platform screen doors (PSDs) in the Seoul Metropolitan Area Railway using 10,078 failure …
본 연구는 2019년부터 2024년까지 18개 노선, 279개 역 10,078건의 고장 기록을 이용하여 수도권 전철 승강장 스크린도어(PSD)의 신뢰성 및 유지보수 성능을 분석한다. 와이블 …
- This study analyzes the reliability and maintenance performance of platform screen doors (PSDs) in the Seoul Metropolitan Area Railway using 10,078 failure records from 279 stations on 18 lines (2019-2024). Weibull lifetime modeling indicates clear wear-out behavior across components (shape parameter β ≈ 1.63-2.30), with electrical stops and motors identified as the most failure-prone elements. Significant manufacturer heterogeneity was observed, with mean time between failures ranging from ≈ 350 to 560 days, underscoring procurement and design effects on lifecycle reliability. A Monte Carlo life-cycle simulation compared four maintenance strategies-reactive, preventive, condition-based, and predictive-under stochastic cost and failure conditions. Condition-based maintenance achieved the lowest 10-year cost (USD 7.9 million) while maintaining availability above 99.6%, whereas predictive maintenance minimized failures and safety incidents at moderately higher cost (USD 9.0 million). Preventive maintenance proved the least efficient under wear-out regimes. The results support a hybrid policy combining predictive thresholds for high-risk modules (motors, electrical stops) with condition-based cycles for lower-risk components. Beyond PSD applications, the validated Weibull-Monte Carlo framework can be reformulated for autonomous and demand- responsive transit (DRT) systems by expressing exposure in operational cycles and adapting cost penalties for missed pickups and availability losses. This transferable reliability-engineering approach provides a quantitative foundation for predictive maintenance and availability optimization in both fixed and mobile, fully driverless transit environments.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 2019년부터 2024년까지 18개 노선, 279개 역 10,078건의 고장 기록을 이용하여 수도권 전철 승강장 스크린도어(PSD)의 신뢰성 및 유지보수 성능을 분석한다. 와이블 수명 모델링은 구성품 전반에 걸쳐 명확한 마모거동(형상 모수 β ≈ 1.63-2.30)을 나타내며, 전기 정지장치와 전동기가 가장 고장 발생 가능성이 높은 요소로 확인되었다. 제조업의 신뢰성은 상당한 이질성이 관찰되었으며, 평균고장간격(MTBF)은 약 350일에서 560일 사이로, 설계가 수명주기 신뢰성에 영향을 미치고 있었다. 몬테카를로 수명주기 시뮬레이션은 확률적 비용 및 고장 조건에서 사후 대응, 예방, 조건 기반, 예측의 4 가지 유지보수 전략을 비교했다. 상태 기반 유지보수는 가용성을 99.6% 이상으로 유지하면서 10년 동안 가장 낮은 비용(790만 달러)을 달성한 반면, 예측유지보수는 다소 높은 비용(900만 달러)으로 고장 및 안전사고가 최소화되었다. 예방 유지보수는 마모 체계에서 가장 비효율적인 것으로 나타났다. 이 결과는 고위험 모듈(모터, 전기 정지 장치)에 대한 예측 임계값과 저위험 구성 요소에 대한 상태 기반 주기를 결합한 하이브리드 정책의 근거가 된다. PSD 적용 외에도, 검증된 Weibull-Monte Carlo 프레임워크는 운영 주기에서의 노출을 표현하고, 픽업 미실시 및 가용성 손실에 대한 비용 페널티를 조정함으로써 자율 주행 및 수요대응 대중교통(DRT) 시스템에 맞게 재구성될 수 있다. 이러한 이전 가능한 신뢰성 공학적 접근 방식은 완전 무인 자율주행 대중교통 환경에서 예측 유지보수 및 가용성 최적화를 위한 정량적 기반을 제공하고 있다.
-
Reliability Analysis of Screen Doors and Door’s Maintenance Strategies for Demand Responsive Self-Driving Shuttles
-
Article
-
A Nested Logit Model of Activity-based Trip Chaining Based on Travel Diary Data of the Autonomous Living Lab in Hwaseong, Gyeonggi
네스티드 로짓 모형을 활용한 활동기반 통행 사슬 모형 개발: 자율주행 리빙랩 통행실태자료를 기반으로
-
YOUM, Juhyoun, AHN, Seonghyun, KIM, Hyunwoo, KIM, Jinhee
염주현, 안성현, 김현우, 김진희
- Conventional Activity-Based Models (ABMs) rely heavily on large-scale datasets to heuristically construct numerous parallel combinations of activities and compute corresponding chains, resulting …
기존의 활동기반모형(Activity-Based Model, ABM)은 방대한 데이터를 기반으로 다양한 활동조합을 병렬적으로 생성하고, 각 활동 간의 사슬을 휴리스틱하게 계산하는 구조를 지님으로써 높은 데이터 의존성을 …
- Conventional Activity-Based Models (ABMs) rely heavily on large-scale datasets to heuristically construct numerous parallel combinations of activities and compute corresponding chains, resulting in a highly data-hungry model structure. To address this limitation, this study proposes an analytical framework that enables the estimation of daily trip chain choices with limited data by endogenously incorporating inter-activity correlations using the Nested Logit model. In particular, the model structurally represents the correlation between work and non-work activities by capturing shared utility components across alternative trip chains. Using one-day travel diary data collected from residents of the Namyang-eup Living Lab in Hwaseong City, several hierarchical nesting structures were examined to identify the most behaviorally and statistically consistent model. The results indicate that the two-level structure separating work-related and other activity nests provides the most valid and interpretable outcomes. The estimated inclusive value parameters confirm the presence of correlated utilities among work-oriented chains, demonstrating improved explanatory and predictive performance compared with the conventional Multinomial Logit model. This study contributes to the advancement of ABM by embedding structural interdependencies among activities, thereby mitigating data dependency while enhancing behavioral consistency and applicability. The proposed model provides a practical methodological foundation for activity-based policy design and Living Lab–oriented travel demand management at the lifestyle-zone level.
- COLLAPSE
기존의 활동기반모형(Activity-Based Model, ABM)은 방대한 데이터를 기반으로 다양한 활동조합을 병렬적으로 생성하고, 각 활동 간의 사슬을 휴리스틱하게 계산하는 구조를 지님으로써 높은 데이터 의존성을 갖는다는 한계가 있다. 이에 본 연구는 네스티드 로짓 모형을 활용하여 활동 간 상관관계를 내생적으로 반영함으로써, 상대적으로 적은 데이터 환경에서도 하루 통행 사슬 선택 행태를 추정할 수 있는 분석모형을 제시하였다. 특히 근로활동과 비근로활동의 결합 여부에 따른 선택 상관성을 구조적으로 반영하여, 활동 유형 간의 효용 공유 구조를 모형화하였다. 연구는 화성시 남양읍 리빙랩 지역에서 수집된 1일 통행일지 자료를 활용하였으며, 다양한 통행 사슬 유형을 대상으로 복수의 계층 구조를 검토하였다. 그 결과, 근로활동을 포함하는 네스트과 기타활동 네스트으로 구분된 2계층 구조가 통계적 타당성과 행태적 해석력 측면에서 가장 우수한 것으로 나타났다. 제시된 모형은 통행 사슬 간 효용의 공유 정도를 Inclusive Value 파라미터를 통해 추정함으로써, 근로활동 중심의 사슬 간 상관성이 존재함을 확인하였다. 이는 기존 다항 로짓 모형에 비해 설명력과 예측력이 모두 향상되었음을 보여준다. 본 연구는 통행 사슬 수준에서의 선택 상관구조를 반영함으로써 데이터 의존적 구조를 완화하고, ABM의 행태적 일관성과 적용성을 동시에 향상시켰다는 점에서 학문적 의의가 있다. 또한, 제안된 모형은 리빙랩 기반의 교통수요관리 및 생활권 단위의 활동기반 정책 수립을 위한 실질적인 분석 도구로 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
A Nested Logit Model of Activity-based Trip Chaining Based on Travel Diary Data of the Autonomous Living Lab in Hwaseong, Gyeonggi
-
Article
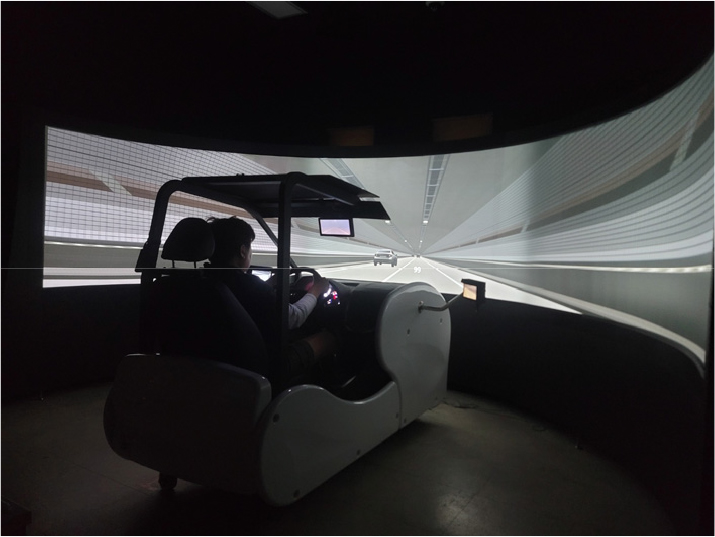

-
Analysis of Driver’s Behavior within the Permission Section for Lane Change of Underground Freeway
지하고속도로 진출을 위한 차로변경 허용구간의 운전자 주행행태 분석 연구
-
LEE, Juehyun, JEONG, Seungwon, LEE, Dongmin
이주현, 정승원, 이동민
- This study experimentally analyzed drivers’ actual lane change behavior within mainline lane change allowance zones of underground freeways and evaluated the validity …
본 연구는 지하고속도로 본선 차로변경 허용구간에서 운전자의 실제 차로변경 행태를 실험적으로 분석하여, 현행 차로변경 허용구간 산정 기준의 타당성을 검증하였다. 현재 「지하도로 설계지침」(MOLIT, …
- This study experimentally analyzed drivers’ actual lane change behavior within mainline lane change allowance zones of underground freeways and evaluated the validity of the current criteria prescribed in design guidelines. The Design Guidelines for Underground Roads (MOLIT, 2023) currently specify lane change allowance zones by directly adopting the criteria developed for tunnels. However, these criteria were empirically derived under tunnel environments, and it remains necessary to verify whether they adequately reflect the actual driving environment and drivers’ perceptual characteristics in underground roads. To address this issue, ground and underground road environments with identical geometric conditions were implemented in a VR driving simulator, and drivers’ lane change initiation point, completion point, lane change distance, and remaining distance were quantitatively compared and analyzed. Under the 400m lane change allowance scenario, lane change initiation and completion in the underground environment occurred significantly later than in the ground environment, resulting in a reduction in remaining distance by more than 90m on average. In contrast, when the lane change allowance zone was extended to 500m by introducing an additional safety buffer, remaining distance recovered and driving stability improved; back-calculation from these results yielded an estimated perception–reaction time of approximately 8 second. These findings experimentally demonstrate that directly applying tunnel-based criteria to underground roads may fail to capture drivers’ delayed perception and decision-making in underground environments, thereby reducing maneuvering margin. Accordingly, lane change allowance zones in underground roads should be redesigned from a fixed-distance criterion to a time-based framework that reflects drivers’ actual perception–reaction times. This study provides quantitative evidence to support such a redesign.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 지하고속도로 본선 차로변경 허용구간에서 운전자의 실제 차로변경 행태를 실험적으로 분석하여, 현행 차로변경 허용구간 산정 기준의 타당성을 검증하였다. 현재 「지하도로 설계지침」(MOLIT, 2023)에서는 차로변경 허용구간을 터널에서의 기준을 준용하고 있다. 그러나 해당 기준은 터널의 환경을 고려하여 경험적으로 산출된 기준으로 실제 지하도로 주행환경과 운전자의 인지 특성을 반영할 수 있는지에 대한 검증이 필요하다. 이에 본 연구는 동일한 기하 조건을 갖춘 지상고속도로와 지하고속도로 환경을 VR 주행 시뮬레이터에서 구현하고, 운전자의 차로변경 시작지점, 종료지점, 차로변경 소요거리, remaining distance를 정량적으로 비교·분석하였다. 분석 결과, 차로변경 허용구간 400m 시나리오에서는 지하의 차로변경 착수 및 완료 시점이 지상보다 유의하게 후행하였으며, 그 결과 remaining distance가 평균 90m 이상 감소하였다. 반면, 여유거리를 적용하여 차로변경 허용구간을 500m로 확대한 조건에서는 remaining distance가 회복되어 주행 안정성이 향상되는 것으로 나타났으며, 이를 역산하면 운전자의 인지반응시간은 약 8초 수준으로 산출되었다. 해당 결과는 터널 기준을 단순히 지하고속도로에 적용하면 운전자의 인지·판단 지연 특성을 반영하지 못해 주행 여유가 부족해질 수 있음을 실험적으로 보여준다. 따라서 지하고속도로의 차로변경 허용구간은 고정된 거리 기준이 아닌 운전자의 실제 인지반응시간을 반영한 시간 기반 설계 체계로 재정립될 필요가 있으며, 본 연구는 이에 대한 정량적 근거를 제시하였다.
-
Analysis of Driver’s Behavior within the Permission Section for Lane Change of Underground Freeway
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation










