-
Article
-
Analysis of Crash Severity Factors in Parking Lots based on TAAS Data
TAAS 데이터 기반 주차장 교통사고 심각도 영향 요인 분석 연구
-
JUNG, Aram, PARK, Hyunsuk
정아람, 박현석
- Parking lots are shared spaces where vehicles and pedestrians. Despite the low speeds, the close interaction between vehicles and pedestrians still presents …
주차장은 차량과 보행자가 혼재되어 있는 공간으로 저속으로 주행한다는 특징이 있으나, 차량과 보행자 간의 근접도가 높아 사고발생 시의 위험성이 크다. 또한 기둥과 같은 …
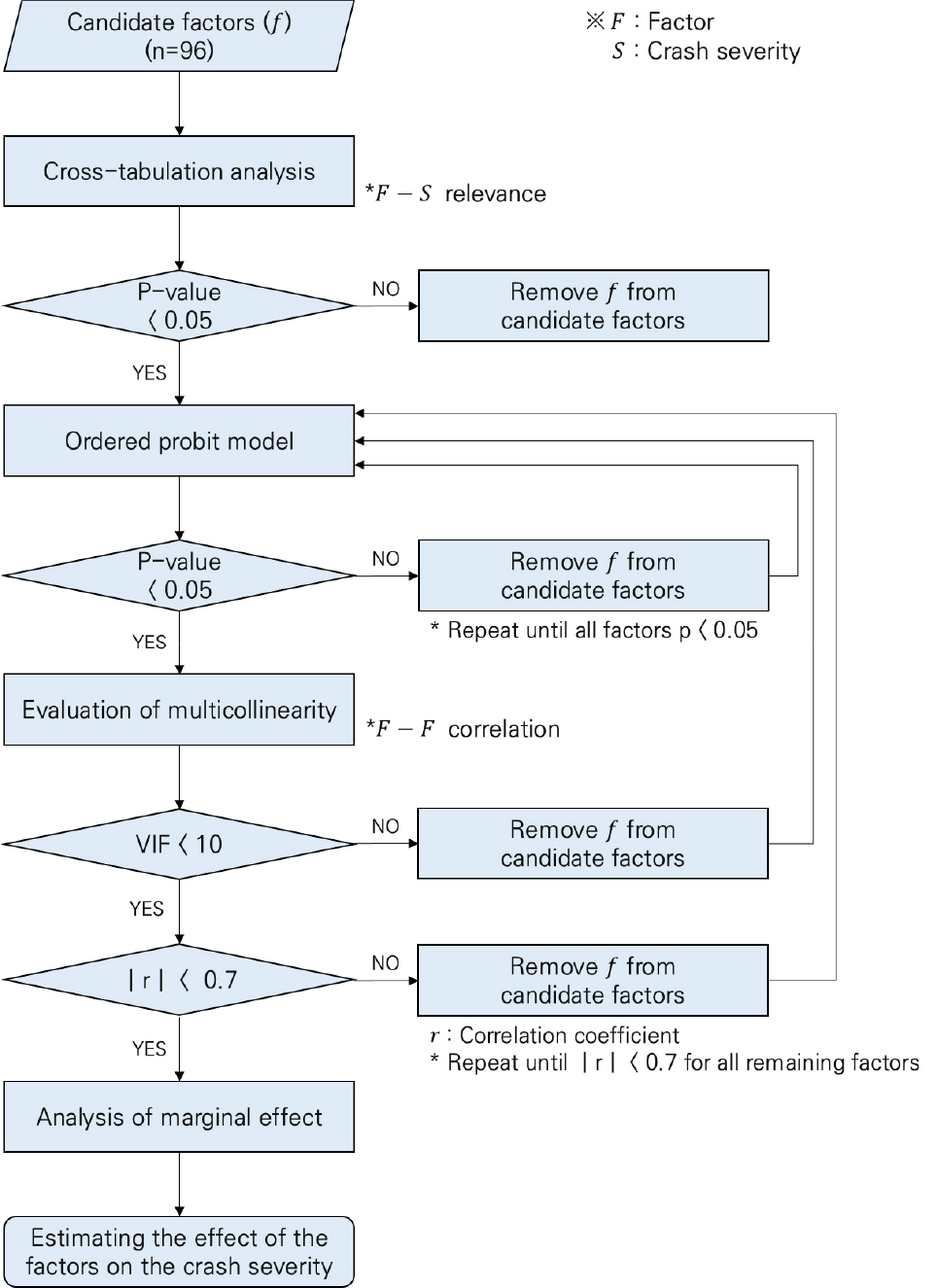
- Parking lots are shared spaces where vehicles and pedestrians. Despite the low speeds, the close interaction between vehicles and pedestrians still presents an high risk of accidents. Furthermore, the presence of pillar and spatial characteristics create blind spots, making parking lots high risk areas where safety evaluation is crucial. The purpose of this study is to identify the factors influencing the severity of parking lot accidents and quantify their impact using statistical methods based on parking lot accident data. For a systematic factor selection, cross-tabulation analysis was performed, and multicollinearity among variables was assessed using the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) and correlation coefficients. An Ordered Probit Model was then developed to derive the accident severity model, and marginal effects were calculated to estimate the probability of each severity level based on the identified factors. The marginal effect analysis revealed that the probability of severe injury or fatality increases when the accident type is vehicle-to-pedestrian, the non at-fault driver’s gender is female, or the age is 51 years or older. Conversely, the probability of minor injury or injury accident increases when the at-fault driver’s vehicle is a motorcycle, bicycle, or scooter, the non at-fault driver’s vehicle is a passenger car or truck, or the non at-fault driver’s age is 30 years or younger. These findings are interpreted as resulting from the spatial characteristics of the parking lot, the characteristics of the at-fault driver's vehicle, and the differences in physical and cognitive capabilities related to the non at-fault driver’s gender and age. The results of this study can be utilized to design control systems or establish customized strategies aimed at preventing parking lot accidents or reducing their severity.
- COLLAPSE
주차장은 차량과 보행자가 혼재되어 있는 공간으로 저속으로 주행한다는 특징이 있으나, 차량과 보행자 간의 근접도가 높아 사고발생 시의 위험성이 크다. 또한 기둥과 같은 물리적 공간 특성으로 인해 사각지대가 발생하여 사고발생 가능성이 높은 공간으로 안전성 평가가 중요하다. 본 연구의 목적은 주차장 교통사고 자료를 기반으로 통계 기법을 통해 주차장 사고 심각도에 대한 영향 요인과 요인의 정량적인 영향 정도를 도출하는 것이다. 체계적인 요인 선정을 위해 교차분석을 통해 사고 심각도와 관련이 있는 변수를 선정하고 분산팽창계수 분석과 상관분석을 통해 요인들 간의 다중공선성을 평가하였다. 순서형 프로빗 모형 분석을 통해 사고 심각도 모형을 도출하고 한계효과를 분석하여 심각도 요인에 따른 사고 심각도별 발생 확률을 산출하였다. 한계효과 분석 결과, 차대사람 사고이거나 피해운전자의 성별이 여성인 경우 그리고 피해운전자가 51세 이상인 경우에는 중상 또는 사망사고 발생 확률이 증가하는 것으로 분석되었다. 반면, 가해운전자 차종이 원동기, 자전거, 이륜차이거나 피해운전자의 차종이 승용차, 화물차인 경우 그리고 피해운전자의 연령이 30세 이하인 경우에는 부상 또는 경상사고 발생 확률이 증가하는 것으로 분석되었다. 이러한 결과는 주차장의 물리적 환경 특성과 가해운전자 차량의 특성 그리고 성별과 연령에 따른 신체적 능력 특성 차이에 의한 것으로 해석되었다. 본 연구의 결과를 활용하여 주차장 사고 예방 또는 심각도 감소를 위한 관제 시스템 설계 또는 맞춤형 전략을 수립할 수 있을 것이다.
-
Analysis of Crash Severity Factors in Parking Lots based on TAAS Data
-
Article
-
Design and Safety Evaluation of a Variable Speed Management Strategy for Small-Vehicle-Only Underground Roads Using Speed Data Pattern Analysis
속도자료 패턴분석 기반 소형차 전용 지하도로 가변형 속도관리전략 설계 및 안전성 평가
-
CUI, Yuanming, LEE, Hoyoon, OH, Cheol, KIM, Jungsik
최원명, 이호윤, 오철, 김정식
- Underground roads create distinctive driving conditions owing to their enclosed spatial configuration and pronounced luminance differences, which can impair driver perception and …
지하도로는 폐쇄적 공간 구조와 내𐄁외부 조도의 차이로 인해 지상도로와는 다른 교통 환경을 형성하며 이러한 특성은 교통안전에 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 특히 고속도로 …
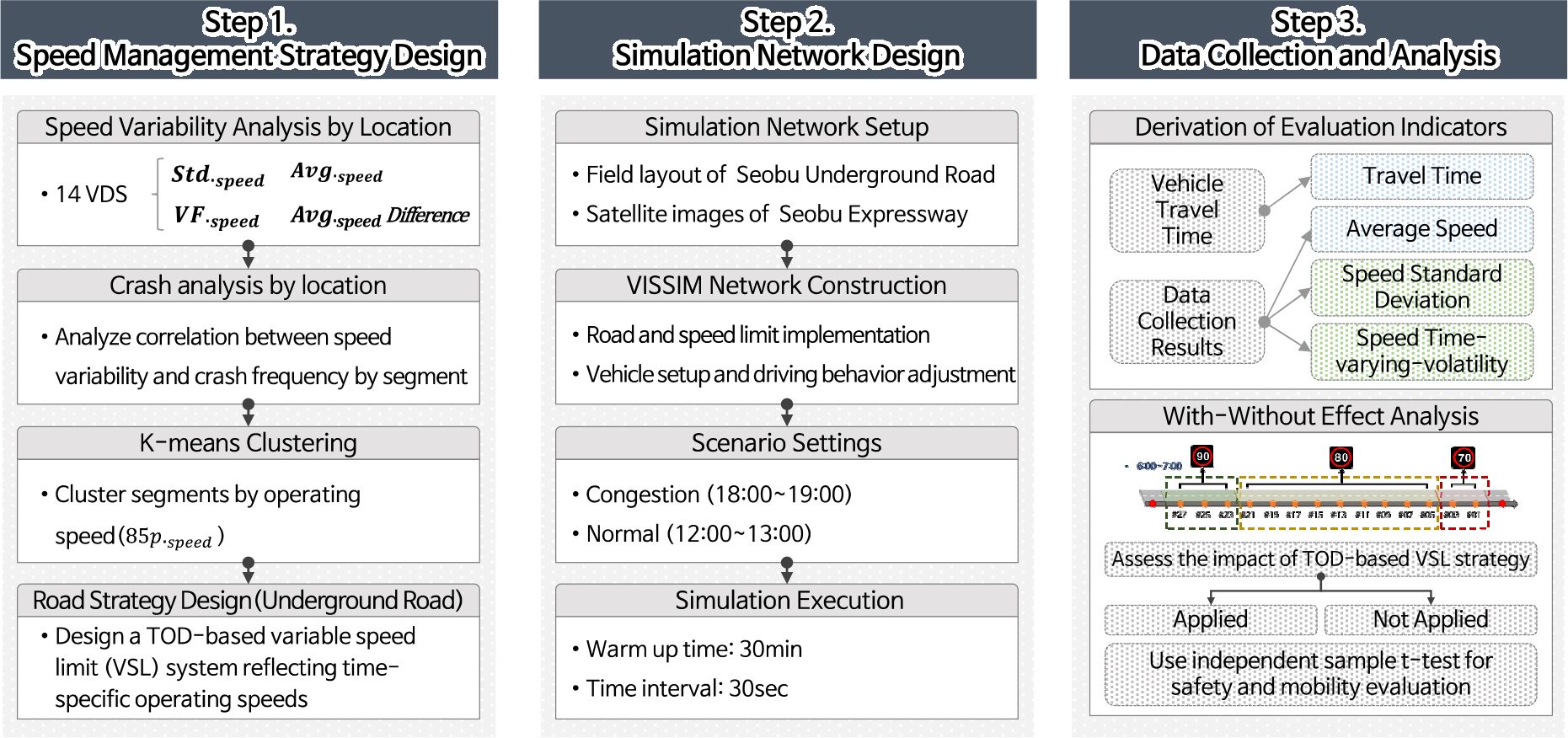
- Underground roads create distinctive driving conditions owing to their enclosed spatial configuration and pronounced luminance differences, which can impair driver perception and increase crash risk. To address these safety concerns, this study proposes a data-driven, time-of-day (TOD)-adaptive Variable Speed Limit (VSL) strategy specifically designed for underground roadways. Utilizing real-world vehicle detector data from the SeoBu Underground Road, operating speeds were calculated at hourly intervals, and K-Means clustering was employed to determine segment- and time-specific speed limits. The proposed strategy was implemented in PTV VISSIM and evaluated under both congestion and normal traffic scenarios. While average travel times exhibited a slight increase in both scenarios because of reduced speed limits. However, the magnitude of this increase was negligible relative to the overall travel times. Notably, substantial improvements in safety were observed: the standard deviation of vehicle speeds in downstream segments declined by 4.5–5.7km/h, and the corridor-wide average decreased by 1.15km/h. In the normal traffic scenario, time-varying volatility of speed was significantly reduced (p = 0.024), with the standard deviation of speed showing a marginally significant trend (p = 0.053). These results demonstrate the VSL strategy’s effectiveness in mitigating speed fluctuations and reducing the incidence of abrupt acceleration and deceleration, thereby enhancing traffic stability and safety. This study identified the limitations of traditional fixed speed enforcement mechanisms (e.g., section speeding enforcement) and the need for adaptive, context-aware speed management systems that consider temporal variations in traffic conditions.
- COLLAPSE
지하도로는 폐쇄적 공간 구조와 내𐄁외부 조도의 차이로 인해 지상도로와는 다른 교통 환경을 형성하며 이러한 특성은 교통안전에 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 특히 고속도로 장대터널과 유사한 특성을 가진 지하도로에서는 사고 발생 시 대형 인명 피해로 이어질 가능성이 크다는 점에서 안전성 확보가 중요하다. 본 연구는 지하도로 교통안전 증진을 위한 실도로 데이터 기반 가변형 속도제한 관리전략을 설계하고 시뮬레이션을 통해 그 효과를 분석하였다. 서부간선지하도로 성산방면 구간에 설치된 차량 검지기 데이터를 바탕으로 1시간 단위 85 백분위 속도를 산출한 후 K-Means 군집분석을 통해 구간별𐄁시간별 제한속도를 설정하여 속도관리전략을 설계하였다. 시뮬레이션 소프트웨어 PTV VISSIM을 활용하여 혼잡 교통상황과 일반 교통상황 두 가지 시나리오를 구성하여 속도관리전략의 효과를 분석하였다. 지하도로 교통류의 안전성 개선 효과 분석을 위해 속도 표준편차와 time-varying-volatility를 활용하였다. 분석 결과, 전략 적용 후 평균 통행시간은 두 가지 시나리오에서 모두 증가하였으나, 제한속도 하향 조정에 따른 감속 운행에 기인한 것으로 실제 통행시간 대비 상대적으로 작은 증가폭으로 나타났다. 반면, 하류부 지점에서는 속도 표준편차가 약 4.5~5.7km/h 감소하였고 전체 표준편차는 1.15km/h 감소하였다. 특히, 일반 교통상황 시나리오에 대한 독립표본 t-검정 결과, 속도 time-varying-volatility는 p = 0.024로 유의수준 0.05에서 통계적으로 유의한 차이를 보였고, 속도 표준편차는 p = 0.053으로 엄격한 유의수준에는 다소 미치지 못했으나 경향성이 관찰되었다. 이는 속도관리전략이 속도 불균형을 완화하고 급가감속 상황을 감소시켜 교통안전 향상에 기여함을 시사한다. 이러한 결과는 현재 시행 중인 단일 제한속도 체계인 구간단속의 한계를 보완하고 시간대별 교통 특성을 반영한 맞춤형 속도관리전략의 필요성과 효과성을 입증한다. 본 연구에서 제안한 속도관리전략은 기존 인프라 기반에 적용 가능성이 높아 지하도로의 실질적인 운영 효율성과 교통 안전성 제고를 위한 정책적 대안으로서의 활용될 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Design and Safety Evaluation of a Variable Speed Management Strategy for Small-Vehicle-Only Underground Roads Using Speed Data Pattern Analysis
-
Article
-
Modeling Real-Time Adaptive Pedestrian Behavior Based on Social Force Model
Social Force Model 기반 실시간 적응형 보행자 행태 모형 개발
-
KIM, Jinsoo, SHIN, Changhoon, PARK, Hoontae
김진수, 신창훈, 박훈태
- This study proposes a real-time adaptive pedestrian behavior model that integrates a speed-based dynamic parameter adjustment algorithm with a visibility-based temporary path …
본 연구는 보행 시뮬레이션의 대표 모형으로 활용되는 사회역학모형(Social Force Model)의 한계를 극복하기 위해 보행자 속도 기반 동적 파라미터 조정 알고리즘과 국지적 가시성 …
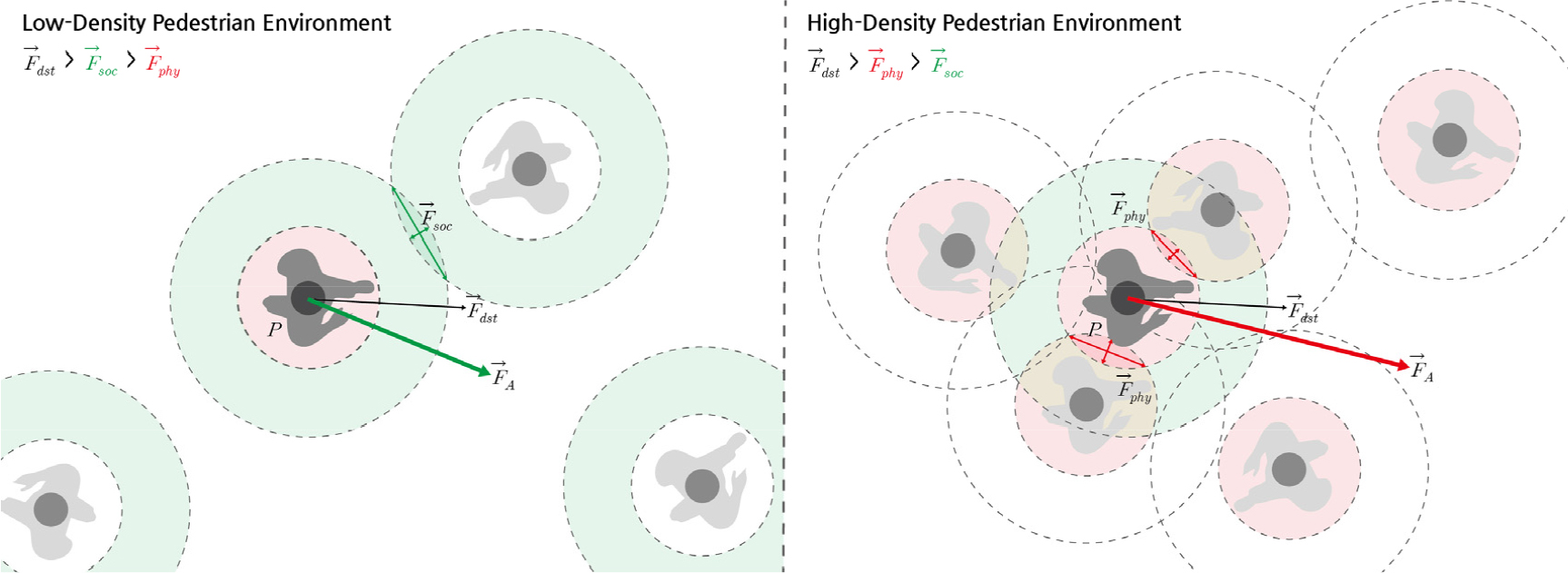
- This study proposes a real-time adaptive pedestrian behavior model that integrates a speed-based dynamic parameter adjustment algorithm with a visibility-based temporary path setting algorithm to overcome the limitations of the conventional social force model, which is widely used in pedestrian simulations. The traditional model, based on fixed parameters, lacks adaptability and fails to reproduce pedestrian behavior realistically in high-density or complex environments. The proposed model addresses these shortcomings by dynamically adjusting key parameters according to the ratio of a pedestrian's current speed to the desired speed and by correcting driving force through visibility-based temporary goal updating. To evaluate its performance, six scenarios―including low and high density, unidirectional and bidirectional flows, bottleneck sections, and complex paths―were designed to compare the proposed model with the conventional model. The results demonstrated that the proposed model outperforms the traditional model in terms of collision avoidance, maintenance of comfort levels, bottleneck passage, and navigation in complex routes. Furthermore, in the validation stage based on empirical comparison using the relationships among pedestrian occupancy space, walking speed, and pedestrian flow, the proposed model consistently produced lower errors than the conventional model, thereby verifying its precision and ability to generalize.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 보행 시뮬레이션의 대표 모형으로 활용되는 사회역학모형(Social Force Model)의 한계를 극복하기 위해 보행자 속도 기반 동적 파라미터 조정 알고리즘과 국지적 가시성 기반 임시 경로 설정 알고리즘을 통합한 실시간 적응형 보행자 행태 모형을 제안한다. 전통적인 사회역학모형은 고정된 파라미터 체계를 전제로 하여 다양한 보행 환경 변화에 대한 적응력이 제한적이며, 특히 고밀도 상황이나 복잡한 경로 조건에서 현실적인 보행 행태를 재현하지 못하는 한계를 지니고 있다. 반면 본 연구에서 제안하는 모형은 보행자의 현재 속도와 목표 속도의 비율에 따라 주요 파라미터를 실시간으로 조정하고, 가시성 영역을 기반으로 임시 목표 방향을 갱신하며 추진력을 보정함으로써 기존 모형의 한계를 보완한다. 본 연구에서는 저밀도/고밀도, 단방향/양방향, 병목 구간, 복잡 경로 등의 6개 시나리오를 설정해 제안 모형과 기존 모형의 성능을 비교 분석하였으며, 분석 결과 제안 모형이 보행자의 회피 기동, 쾌적 상태 확보, 병목 통과, 복잡 경로 진행 부문에서 월등한 성능을 보였다. 또한 보행점유공간, 보행속도, 보행교통류율의 관계식에 기반하여 실증 데이터를 통한 유효성 검증 단계에서도 제안 모형이 기존 모형과 비교하여 일관되게 낮은 오차를 보임으로써 모형의 정밀성 및 일반화 가능성을 입증하였다.
-
Modeling Real-Time Adaptive Pedestrian Behavior Based on Social Force Model
-
Article
-
Analyzing the Safety Impact of Tunnel Traffic Safety Facilities Using Structural Equation Modeling
구조방정식 모형 기반 터널 교통안전시설 유형별 안전 기여도 분석
-
CHOI, Borim, CHUNG, Younshik, KIM, Sangsu, KIM, Junggeun
최보림, 정연식, 김상수, 김정근
- Recently, due to the construction of new tunnels, the extension of existing tunnels, and the construction of underground expressways, the demand for …
최근 터널 신설 및 장대화, 지하고속도로 건설 등으로 인해 터널 교통안전 대책 마련을 위한 첨단 기술 도입 요구가 증가하고 있다. 이에 한국도로공사에서는 …
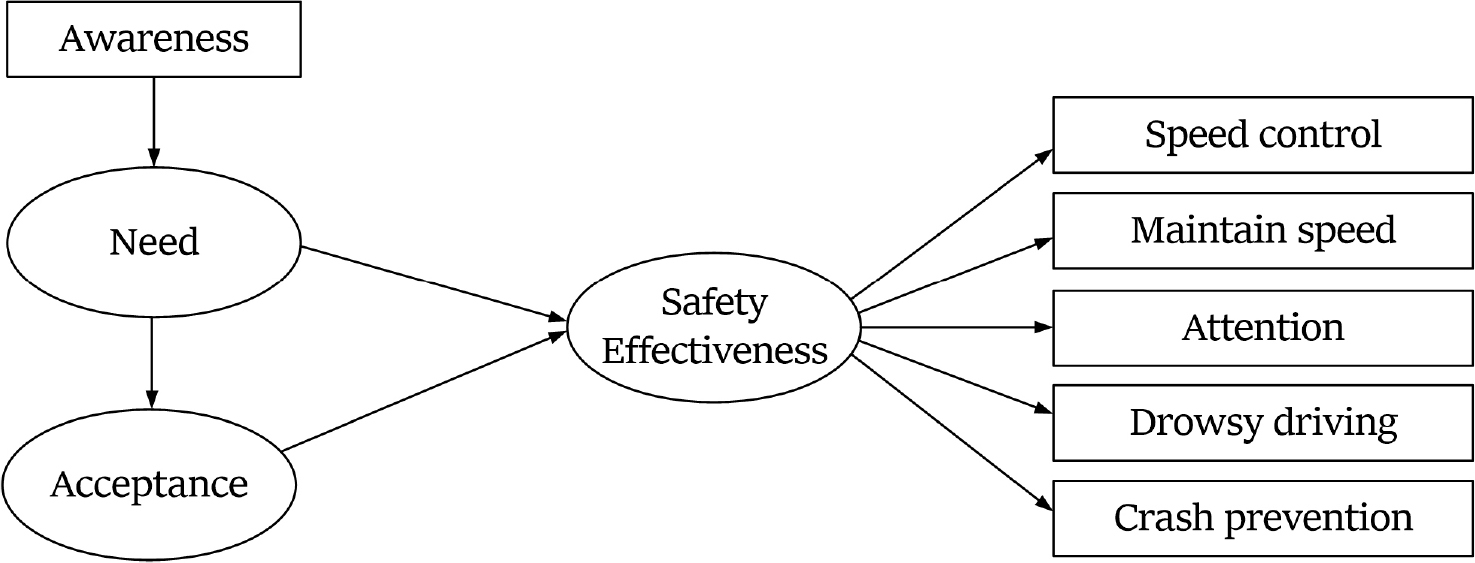
- Recently, due to the construction of new tunnels, the extension of existing tunnels, and the construction of underground expressways, the demand for introducing advanced technologies to enhance tunnel traffic safety measures has increased. The traffic safety facility currently deployed in domestic tunnels contribute to traffic safety in different ways, depending on their specific characteristics. A better understanding of how each facility enhances safety can lead to more efficient utilization. Therefore, this study examines the characteristics of key traffic safety facility—VMS (Variable Message Sign), LCS (Lane Control System), VGS (Voice Guidance System), and LEDLS (Light Emitting Diode Lighting System)—used in domestic tunnels, with the aim of identifying their individual contributions to traffic safety and laying the groundwork for their effective use. To this end, a survey was conducted among drivers who had experienced the tunnel traffic safety facility to analyze the relationship between drivers’ 'awareness', 'need', and 'acceptance' of the facility, and the facility’s 'safety effectiveness'. As a result, it was found that 'awareness' of the facility had a positive effect on 'need', and 'need' had a positive effect on 'acceptance'. In addition, it was found that the 'safety effectiveness' varied depending on the purpose of the facility installation. In the case of facilities whose main purpose is to ‘provide traffic situation information’ to drivers (VMS, LCS), the 'need' for the facility had a positive indirect effect on 'safety effectiveness' through 'acceptance', and 'acceptance' had a direct effect on 'safety effectiveness'. On the other hand, in the case of facilities whose main purpose is to ‘attention-raise drivers’ (VGS, LEDLS), the 'need' for the facility had a direct effect on 'safety effectiveness', and 'acceptance' did not seem to affect 'safety effectiveness'.
- COLLAPSE
최근 터널 신설 및 장대화, 지하고속도로 건설 등으로 인해 터널 교통안전 대책 마련을 위한 첨단 기술 도입 요구가 증가하고 있다. 이에 한국도로공사에서는 터널 교통안전시설을 도입하여 안전한 도로 환경을 조성하고자 노력을 기울였고, 지난 10년간 국내 터널 교통사고 발생률은 연평균 1.7% 감소하였다. 그러나 같은 기간 사망자 수는 증가하여 보다 효과적인 터널 교통안전 대책 마련이 필요한 실정이다. 현재 국내 터널에 구축된 교통안전시설은 각 시설별 특성에 따라 교통안전에 기여하는 정도가 다르게 나타날 것이며, 각 시설별 특성에 따른 교통안전 기여도를 파악함으로써 시설의 효율적인 활용 가능성이 증가할 것이다. 이에 본 연구에서는 국내 터널에 구축된 주요 교통안전시설인 교통안전표지판, 차로제어시스템, 음성안내시스템, LED 면조명시스템의 특성을 고려하여 시설별 교통안전 기여도를 파악함으로써 개별 시설의 효율적 활용을 위한 기반을 마련하고자 한다. 이를 위해 터널에 설치된 주요 교통안전시설을 경험한 운전자를 대상으로 설문조사를 수행하여 각 시설에 대한 운전자들의 ‘인지도’, ‘필요성’, ‘수용도’가 ‘교통안전 기여도’에 미치는 영향 관계를 파악하였다. 그 결과, 운전자에게 ‘교통상황 정보 전달’이 주목적인 시설의 경우, 시설에 대한 필요성은 수용도를 매개하여 교통안전 기여도에 긍정적인 간접영향을, 수용도는 교통안전 기여도에 긍정적인 직접영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 반면, ‘운전자 주의 환기’가 주목적인 시설의 경우, 시설에 대한 필요성은 교통안전 기여도에 긍정적인 직접영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났으며, 수용도는 교통안전 기여도에 영향을 미치지 않는 것으로 나타났다.
-
Analyzing the Safety Impact of Tunnel Traffic Safety Facilities Using Structural Equation Modeling
-
Article
-
A Study on MMA Based Anti-skid Pavement Materials with Deicing Functionality
결빙방지 기능을 갖는 MMA계 미끄럼방지포장재의 관한 연구
-
CHO, Yongsang, PARK, Kuiyoung, CHANG, Iljoon
조용상, 박규영, 장일준
- This study aims to develop and evaluate an anti-icing type anti-skid pavement material based on methyl methacrylate (MMA) resin to prevent traffic …
본 연구는 겨울철 노면의 결빙으로 인한 교통사고를 예방하기 위해 MMA(Methyl methacrylate)계 수지를 기반으로 한 결빙방지형 미끄럼방지포장재를 개발하고 성능을 평가하였다. 결빙방지 소재의 혼입에 …
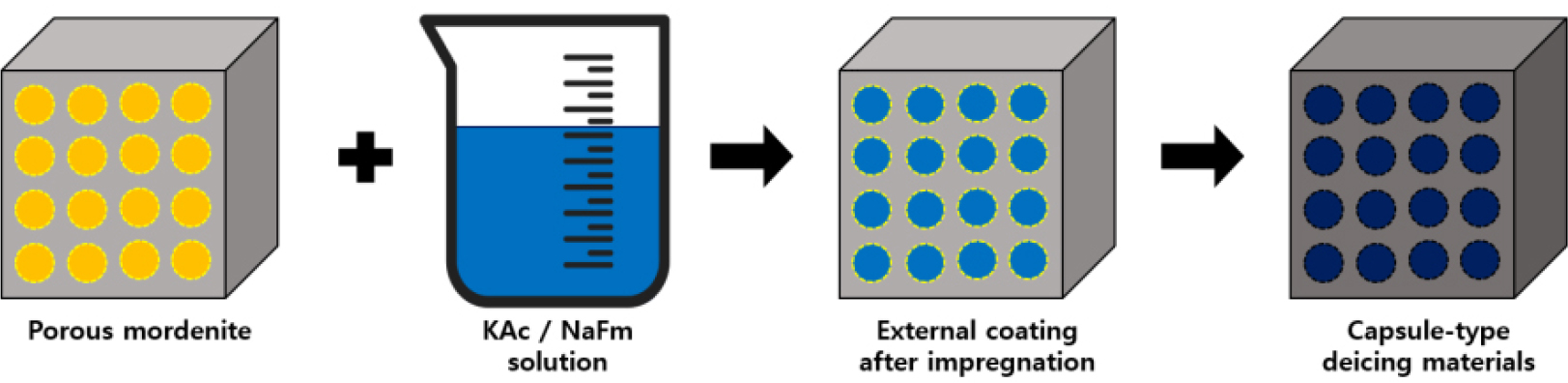
- This study aims to develop and evaluate an anti-icing type anti-skid pavement material based on methyl methacrylate (MMA) resin to prevent traffic accidents caused by road surface icing during winter. To minimize performance variation due to the incorporation of anti-icing agents, an optimized MMA–BA–2-HEMA ternary resin system was designed as the base binder. Encapsulated organic salt-based anti-icing materials (potassium acetate, sodium formate, and a potassium acetate/sodium formate blend) were incorporated into the pavement mixture to fabricate the anti-icing type anti-skid pavement. Mechanical performance tests revealed that the addition of encapsulated anti-icing agents did not reduce adhesion strength, compressive strength, or abrasion resistance, showing comparable results to the plain specimens. This indicates that the encapsulated organic salts do not negatively affect the mechanical properties of the pavement. In the anti-icing performance tests, potassium acetate exhibited the fastest melting rate, while the potassium acetate/sodium formate blend demonstrated enhanced ion diffusion and melting persistence, indicating improved long-term anti-icing performance. The ice adhesion strength decreased in all specimens containing encapsulated anti-icing materials compared to the plain specimens. Furthermore, after 30 freeze–thaw cycles, all specimens exhibited approximately 7% reduction in compressive strength, regardless of the type or dosage of anti-icing material, confirming that the encapsulated agents did not induce structural degradation. Overall, the anti-icing type anti-skid pavement material developed in this study demonstrates both mechanical stability and durable anti-icing performance, suggesting its potential to improve road safety and maintenance efficiency during winter conditions.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 겨울철 노면의 결빙으로 인한 교통사고를 예방하기 위해 MMA(Methyl methacrylate)계 수지를 기반으로 한 결빙방지형 미끄럼방지포장재를 개발하고 성능을 평가하였다. 결빙방지 소재의 혼입에 따른 미끄럼방지포장재의 성능변화를 최소화하기 위해 MMA·BA·2-HEMA 3성분계의 최적 비율 MMA계 수지를 기반으로 미끄럼방지포장재의 배합을 설계하였으며, 캡슐화 공정을 통해 제조된 유기염계 결빙방지 소재(초산칼륨, 포름산나트륨, 초산칼륨+포름산나트륨 혼합)를 미끄럼방지포장재에 혼입하여 결빙방지형 미끄럼방지포장재를 제조하였다. 기계적 성능 평가 결과 캡슐화된 유기염계 결빙방지 소재의 혼입에 따른 접착강도, 압축강도 및 내마모성의 저하는 없었으며 표준규격을 상회하는 수준을 보여 캡슐화된 유기염계 결빙방지 소재의 혼입은 기계적 성능 특성에 부정적인 영향을 주지 않는 것으로 확인되었다. 결빙방지 성능 시험에서는 초산칼륨이 가장 빠른 융빙속도를 보였고, 초산칼륨+포름산나트륨 혼합형은 융빙 지속성 및 이온 확산성이 향상되어 장기적인 결빙방지 성능을 확보할 수 있음을 확인하였다. 빙착 접착력은 모든 캡슐화된 유기염계 결빙방지 소재의 혼입군에서 PLAIN 대비 감소되는 경향을 나타내었다. 또한 동결 노화 가속 시험 후 모든 시험편에서 약 7%의 압축강도 감소가 관찰되었으며 결빙방지 소재의 유무나 혼입률과 관계 없는 경향을 보여 캡슐화된 결빙방지 소재가 구조적 손상을 유발하지 않음을 의미한다. 종합적으로 본 연구에서 평가된 결빙방지형 미끄럼방지포장재는 기계적 안정성과 장기적 결빙방지 성능을 동시에 확보할 수 있는 복합 기능성 포장재로서, 겨울철 도로의 교통안전성 향상과 유지관리 효율성 제고에 기여할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
A Study on MMA Based Anti-skid Pavement Materials with Deicing Functionality
-
Article
-
Estimating Capacity Adjustment Factors for Highway Basic Segments under Autonomous Vehicle Penetration
자율주행차량 혼입을 고려한 고속도로 기본구간 용량 보정계수 산정 연구
-
BAEK, Seongchae, MOON, Junhyeong, YUN, Jeongin, SHIN, Chihyun, LEE, Jinwoo, PARK, Jejin
백성채, 문준형, 윤정인, 신치현, 이진우, 박제진
- This study quantifies the impacts of autonomous vehicle (AV) penetration and driving behavior on the capacity of freeway basic segments and develops …
본 연구는 자율주행차의 혼입률과 주행행태가 고속도로 기본구간 용량에 미치는 영향을 정량화하고, 국내 도로용량편람 체계에 호환되는 용량 보정계수(CAF)를 제시한다. 대표 기본구간(제한속도 100/120km/h)을 실측 …
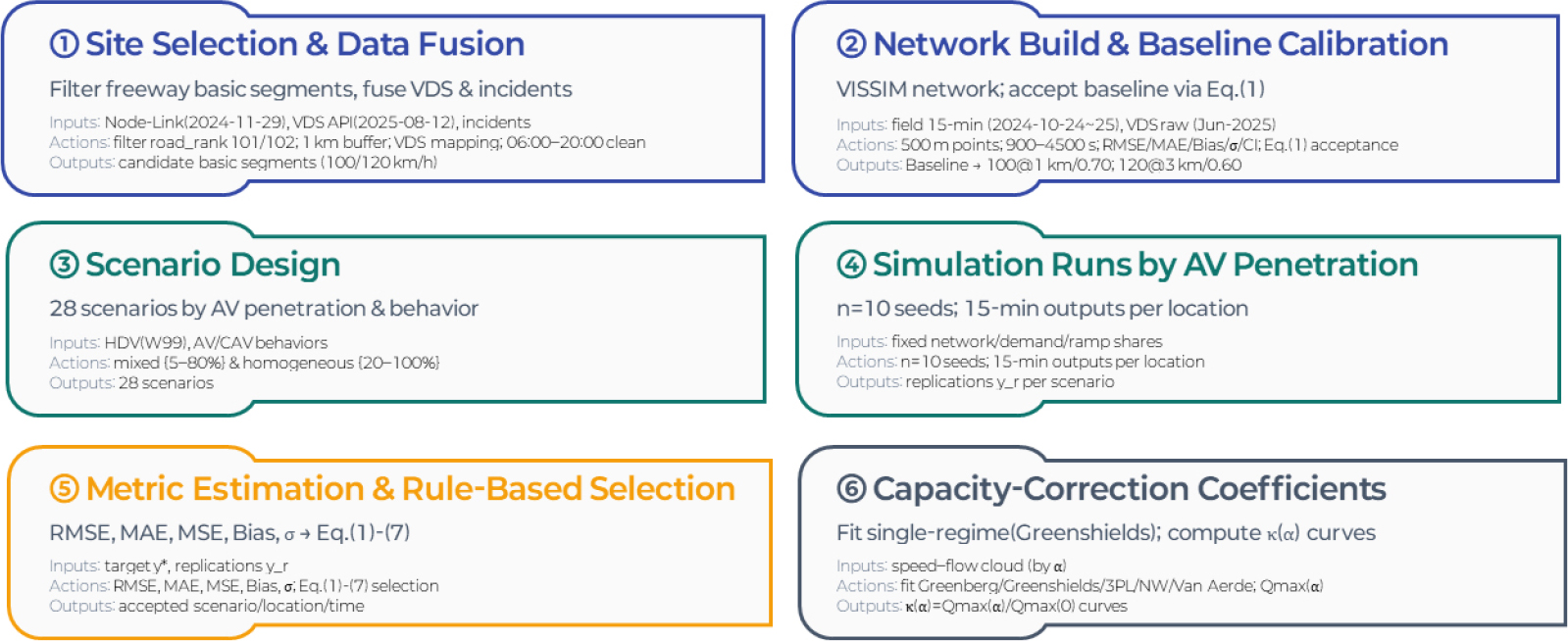
- This study quantifies the impacts of autonomous vehicle (AV) penetration and driving behavior on the capacity of freeway basic segments and develops Highway Capacity Manual compatible capacity adjustment factors (CAFs) for Korean practice. Using field data, we selected and calibrated representative basic segments (speed limits: 100/120km/h), then ran 25 VISSIM scenarios (AV penetration α=0-1; behaviors: Cautious/Normal/Aggressive/CAV). Baseline calibration relied on RMSE, MAE, bias, and standard deviation. Capacity was defined as the per-lane maximum flow (pcphpl) from single-regime Greenshields fits. For the 100km/h site, CAV yielded the largest gains, reaching 2,804 pcphpl at α=1.0 (CAF=1.268), while Aggressive and Normal produced more modest improvements with CAFs of 1.083 and 1.038 at α=1.0, respectively. In contrast, Cautious decreased monotonically with penetration, reducing capacity to 1,584 pcphpl (CAF=0.72) at α=1.0. At 120km/h, CAV again provided the strongest benefits, reaching 2,836 pcphpl (CAF=1.24 at α=1.0), whereas Aggressive and Normal showed moderate gains (maximum CAFs =1.08 and 1.05). Cautious reduced capacity further to 1,368 pcphpl (CAF=0.60). Mixed-behavior CAF curves consistently lay between the CAV upper and Cautious lower bounds, offering realistic planning ranges for mixed traffic. The contributions are threefold: (i) a rule-based baseline calibration procedure for representative sites, (ii) empirically derived CAF curves and values by penetration and behavior, and (iii) a clear pathway to incorporate AV effects into KHCM-style analyses.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 자율주행차의 혼입률과 주행행태가 고속도로 기본구간 용량에 미치는 영향을 정량화하고, 국내 도로용량편람 체계에 호환되는 용량 보정계수(CAF)를 제시한다. 대표 기본구간(제한속도 100/120km/h)을 실측 자료 기반으로 선별·정산한 뒤, VISSIM에서 혼입률(α=0-1)과 주행행태(Cautious, Normal, Aggressive, CAV)를 교차 설계한 25개 시나리오를 수행하였다. 정산은 RMSE·MAE·Bias·반복 표준편차를 이용해 기준 시나리오를 확정하고, 용량은 Greenshields 단일체제 모형에서 얻은 차로당 최대교통류(pcphpl)로 정의하였다. 100km/h 대상지에서는 CAV가 α=1.0에서 2,804 pcphpl(CAF=1.268)에 도달하여 가장 큰 이득을 보였고, Aggressive와 Normal은 각각 CAF=1.083, 1.038(α=1.0 기준) 수준의 완만한 개선을 나타냈다. 반대로 Cautious는 혼입률이 증가할수록 일관되게 감소하여, α=1.0에서 1,584 pcphpl(CAF=0.72)까지 용량이 축소되었다. 120km/h 대상지에서도 CAV 효과가 가장 크게 나타나 α=1.0에서 2,836 pcphpl(CAF=1.24)에 도달하였으며, Aggressive와 Normal은 최대 CAF가 각각 약 1.08, 1.05 수준의 중간 정도 개선 효과를 보였다. Cautious는 α=1.0에서 1,368 pcphpl(CAF=0.60)까지 용량을 저하시켰다. 혼합행태 시나리오의 CAF 곡선은 전 구간에서 CAV 상한과 Cautious 하한 사이에 위치하여, 현실적인 혼합교통류에서 기대 가능한 계획·운영 범위를 제시한다. 본 연구는 (i) 대표 구간의 규칙 기반 정산 절차, (ii) 혼입률·주행행태별 CAF 곡선·값, (iii) KHCM/도로용량편람에 AV 효과를 접목하는 적용 경로를 제시함으로써 향후 기준 개정의 정량적 근거를 제공한다.
-
Estimating Capacity Adjustment Factors for Highway Basic Segments under Autonomous Vehicle Penetration
-
Article
-
A Comparative Study on AI-Based Pseudonymization Methods for Safe Utilization of Transportation Complaint Texts
교통 민원 텍스트의 안전한 활용을 위한 AI 기반의 가명처리 비교 연구
-
KIM, Keunwook, CHUNG, Younshik
김건욱, 정연식
- Local governments increasingly rely on civil complaint data to inform urban policymaking; however, the presence of personal information and offensive language significantly …
도시 내 사회문제를 해결하기 위해 대부분의 지자체는 민원 데이터를 정책 근거로 활용하고 있으나, 민원 텍스트에는 주소·차량번호·이름 등 개인정보와 공격적 표현, 비속어가 함께 …
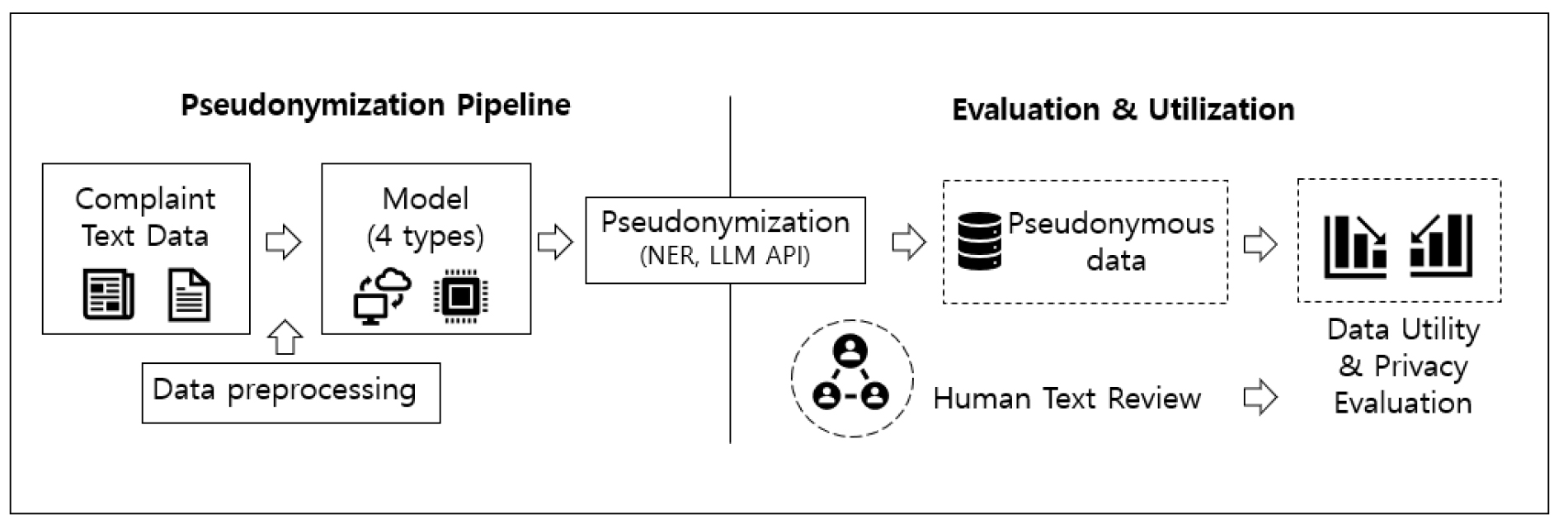
- Local governments increasingly rely on civil complaint data to inform urban policymaking; however, the presence of personal information and offensive language significantly restricts data sharing and public disclosure. Although pseudonymization techniques based on regular expressions or named entity recognition (NER) are widely adopted, they often inadequately preserve contextual meaning and fail to balance data utility with privacy protection. This study proposes a secure and practically applicable pseudonymization framework and conducts a quantitative comparison of alternative approaches. The analysis is based on 4,889 traffic-related civil complaints collected in Daegu Metropolitan City between December 2023 and March 2025. Four methods are evaluated: NER-based substitution, synthetic text generation using a multilingual language model (Qwen 2.5), synthetic text generation using a Korean-specific language model (EXAONE 3.5), and an “intentional recombination” approach that reconstructs complaint texts by reorganizing key nouns and verbs according to the complaint title as an explicit representation of intent. The results indicate that while the NER-based method most closely preserves the original textual structure and word distribution, it exhibits a comparatively high residual rate of personal information and profanity. By contrast, the Korean language model–based intentional recombination approach achieves the lowest residual rate (5.27%) while maintaining approximately 94% semantic similarity to the original texts. Multilingual language models demonstrate limitations for practical deployment due to contextual distortion and unintended foreign language mixing. These findings suggest that Korean-specific language models combined with intent-based reconstruction provide an effective foundation for the secure utilization of traffic complaint data in local governments and highlight the need for further research to generalize this framework across other urban policy domains.
- COLLAPSE
도시 내 사회문제를 해결하기 위해 대부분의 지자체는 민원 데이터를 정책 근거로 활용하고 있으나, 민원 텍스트에는 주소·차량번호·이름 등 개인정보와 공격적 표현, 비속어가 함께 포함되어 있어 제3자 제공이나 개방에 한계가 있다. 이에 따라 정규표현식이나 개체명 인식 모형을 활용한 텍스트 가명처리가 널리 사용되고 있으나, 문맥을 충분히 반영하지 못하거나 데이터 유용성과 개인정보 보호 간 균형을 맞추는 데 어려움이 존재한다. 본 연구는 공간적으로 대구광역시, 시간적으로 2023년 12월부터 2025년 3월까지 수집된 교통 민원 텍스트 4,889건을 대상으로 현업에서 활용 가능한 안전한 가명처리 방법을 제시하고, 이를 정량적으로 비교·평가하고자 한다. 비교 대상 모형은 ① 개체명 인식(NER) 기반 치환 모델, ② 다국어 언어모델 기반 합성데이터 생성(Qwen 2.5), ③ 한국어 특화 언어모델 기반 합성데이터 생성(EXAONE 3.5), ④ 민원 제목을 ‘의도’로 간주하고 본문 내 핵심 명사·동사를 재조합하여 문장을 재작성하는 ‘의도 재조합’ 기반 한국어 언어모델(EXAONE 3.5)이다. 데이터 유용성과 개인정보 보호 관점에서 분석한 결과, 개체명 인식 방법은 원문 구조와 단어 분포를 가장 유사하게 유지하였으나, 개인정보 및 비속어 잔여 비율이 상대적으로 높게 나타났다. 반면 제안한 한국어 언어모델 기반 ‘의도 재조합’ 방식은 잔여 개인정보·비속어 비율이 5.27%로 가장 낮게 나타났고, 원문 문장의 의미 유사도도 약 94% 수준으로 유지되는 것을 확인하였다. 다국어 언어모델의 경우 문맥 왜곡과 외국어(중국어) 혼합 등이 발생하여 실제 현업에 적용하기에는 한계가 있는 것으로 나타났으며, 이러한 결과는 한국어 특화 언어모델과 의도 기반 재구성 접근이 지자체 교통 민원 데이터의 안전한 데이터 활용에 있어 주요한 기초 연구가 될 것으로 판단되며, 향후 도시내 다양한 분야로 일반화되기 위해 후속 연구의 필요성도 함께 제시하였다.
-
A Comparative Study on AI-Based Pseudonymization Methods for Safe Utilization of Transportation Complaint Texts
-
Article
-
Key Determinants of Ridership of Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit Services: Empirical Evidence from the Gyeonggi Metropolitan Bus Service
광역형 수요응답형 대중교통의 승차 수요 영향요인 분석: 경기도 광역콜버스 사례를 중심으로
-
SEO, Youngwoon, YOU, Soyoung Iris, KOH, Keonwoo, HEO, Changjun, OH, Wonjun, JO, Hanghun, CHOI, Sungtaek
서영운, 유소영, 고건우, 허창준, 오원준, 조항훈, 최성택
- This study empirically examines the determinants of boarding demand for the Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit (M-DRT), a demand-responsive public transport service linking …
본 연구는 서울과 서울 인접 도시를 연결하는 광역형 수요응답형 대중교통(Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit, 이하 M-DRT)을 대상으로 정류장별, 노선별, 월별 이용 실적 자료를 …
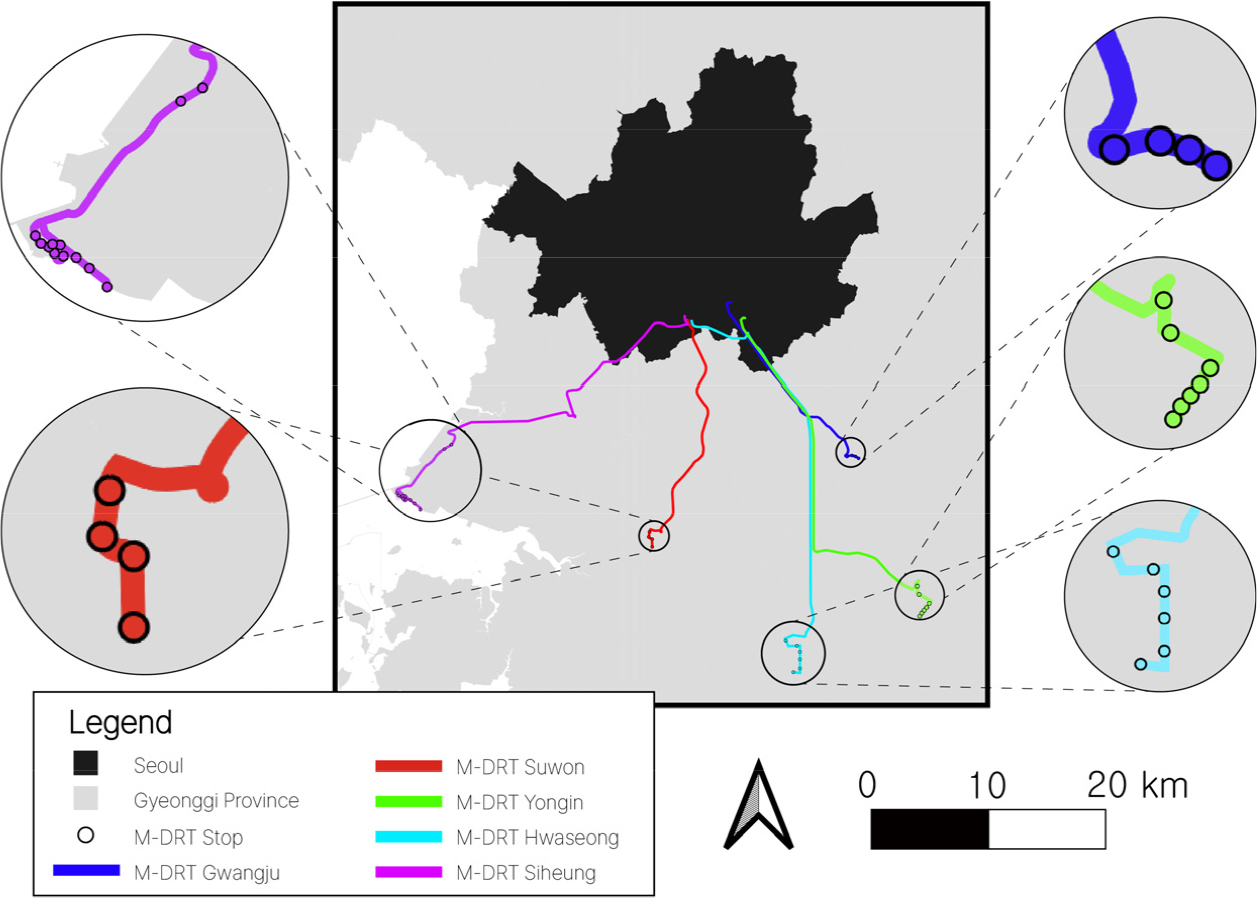
- This study empirically examines the determinants of boarding demand for the Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit (M-DRT), a demand-responsive public transport service linking Seoul with the nearby peri-urban area. Using operational data from October 2023 to July 2025, we constructed explanatory variables incorporating the number of new and frequent users in the previous month, land-use and transit connectivity around stops, and weather and operational attributes. A random-effects negative binomial regression model was applied to accommodate the count nature of the dependent variable and unobserved heterogeneity across stops. The results show that land-use mix, bus transfer accessibility, and operating duration have significant positive effects on boarding demand. Notably, the influence of the number of frequent users in the previous month exceeds that of new users, indicating that retaining repeat users is essential for securing long-term demand stability. This suggests that preference for M-DRT strengthens through repeated rather than occasional use. Additionally, the positive effect of bus transfer accessibility implies that M-DRT serves as a complementary transfer-based mode rather than a competitor to existing public transport. By identifying the causal contribution of a frequent user base to demand formation using real operational records, this study highlights the importance of customer retention strategies and strengthened transfer connectivity in future planning and policy design for M-DRT services.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 서울과 서울 인접 도시를 연결하는 광역형 수요응답형 대중교통(Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit, 이하 M-DRT)을 대상으로 정류장별, 노선별, 월별 이용 실적 자료를 토대로 버스 승차 수요의 영향 요인을 실증적으로 분석하였다. 2023년 10월부터 2025년 7월까지의 실제 운영데이터를 활용하였으며, 수요의 영향 요인으로 전월 신규 이용자 및 다빈도 이용자 규모를 고려한 이용자 특성, 정류장 주변의 토지이용 및 교통 연계성, 기상 및 운영 특성을 설명변수로 설정하였다. 종속변수의 특성과 정류장 고유 특성을 통제하기 위해 랜덤효과 음이항 회귀 모형을 적용한 결과, 토지이용 혼합도, 버스 환승 접근성, 운영 기간이 승차 수요 증가에 유의한 양(+)의 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 특히 전월 다빈도 이용자 수의 영향력은 신규 이용자보다 크게 나타나 반복 이용자의 유지가 장기적 수요 안정성 확보에 핵심적임을 확인하였다. 이는 M-DRT가 일회성 이용보다는 반복적 이용을 통해 선호가 강화되는 서비스 구조를 갖는다는 점을 시사한다. 또한 버스 수단 접근성 이용 수요에 양의 영향력을 가져 M-DRT가 기존 대중교통과 경쟁하기보다는 환승 기반 보완 수단으로 기능할 수 있음을 보여준다. 본 연구는 실제 운영데이터 기반의 계량 분석을 통해 M-DRT 서비스에서 다빈도 이용자 기반의 수요 형성 인과관계를 규명했다는 점에서 의의를 지니며, 향후 M-DRT 운영 계획 및 정책 수립 과정에서 고객 유지 전략과 환승 연계성 강화가 수요 안정성 확보의 핵심임을 시사한다.
-
Key Determinants of Ridership of Metropolitan Demand Responsive Transit Services: Empirical Evidence from the Gyeonggi Metropolitan Bus Service
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of Korean Society of Transportation
Journal of Korean Society of Transportation










